This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
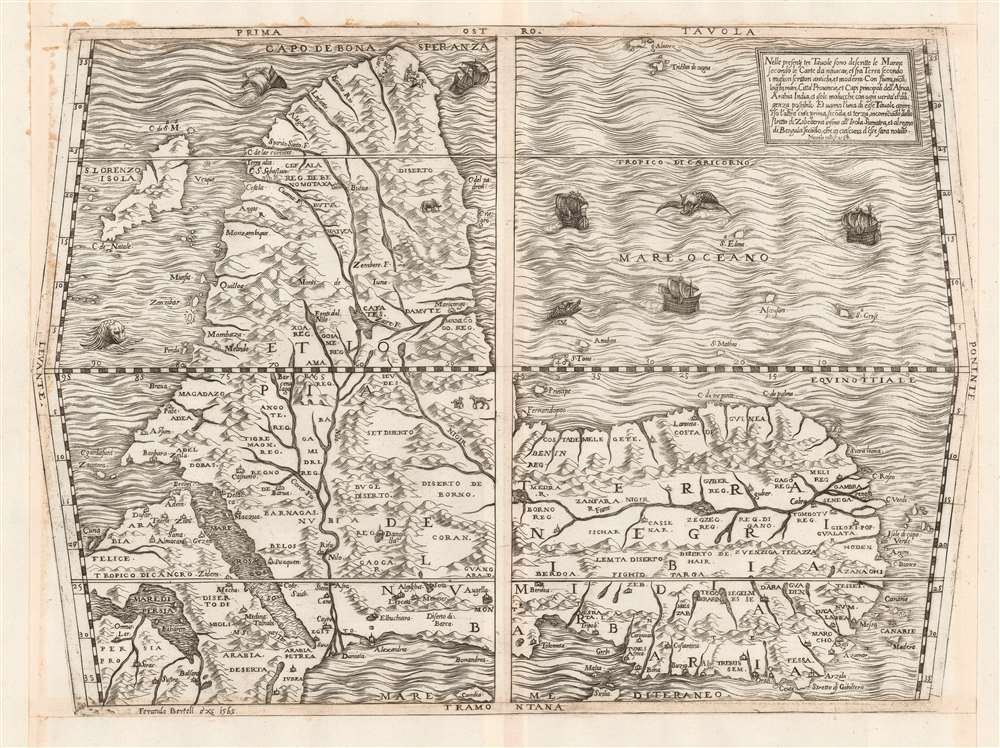
1564 Bertelli / Gastaldi map of Africa
Africa-bertelli-1564
Title
1564 (dated) 11.25 x 15.5 in (28.575 x 39.37 cm) 1 : 30000000
Description
Rich Detail
Gastaldi's cartography represented a sharp advance on that of Münster, which preceded the first version of this map by fourteen years. Much of this map's detail is derived from Portuguese sources, including Montalbodo's accounts of the voyages of Cadamosto, Da Sintra, and Da Gama. The map's northern and interior portions are taken from the Arab geographer al Hassan Ibn Muhammad al Wazzan, known to European geographers as Leo Africanus. The map's depiction of the Nile has its sources in the Ptolemaic lakes in the mountains of the moon, with an additional river flowing south from Lake Zaire to feed both the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. This is among the earliest maps of the African continent to include Madagascar, whose inclusion is probably drawn from Diogo Dias' reports.The Niger River is illustrated flowing east-to-west, fed by an unnamed lake south of the Equator. Timbuctu (Tombotu) is identified, though appearing much too far to the west. The Portuguese trade fort El Mina is labeled as well (Lamina, on the map).
Beautifully Engraved
This map - a copperplate engraving, as opposed to the earlier woodcuts from which it is derived - is notable for its decorative elements. Amongst the mountains pictorially represented in the body of the map can be found an elephant, a pair of leopards just north of the equator, and a herd of what might be wildebeest in the south part of the continent. Dangers abound. The sea is prowled by three monsters, and of the five sailing ships, two - those nearest the Cape of Good Hope - appear to be sinking.Maps of the 'Lafreri' School
Between 1544 and the 1580s, Rome and Venice saw the production of a number of elegant, rare, and consequently now sought-after maps. These are frequently classified collectively as belonging to the 'Lafreri-School,' a term often used due to the survival of a 1572 catalog of maps from the stock of publisher Antonio Lafreri. The close resemblance of this list to the contents of various bound collections of Roman and Venetian maps of the period led to these proto-atlases to be attributed to Lafreri, despite the maps having been actually produced by over a dozen different mapmakers, including Gastaldi, Lafreri himself, his heir Duchetti, the Bertellis, Camochio, Zenoni, Salamanca, Forlani, Ligorio, Tramezini, Zaltieri and others. These cartographers, mapmakers, engravers, and publishers, some of whom shared formalized partnerships, left behind a legacy of some six or seven hundred maps, all of which are marked by scarcity due to their not having been included in a standard atlas. Though these were generally sold in assembled-to-order, composite 'atlases,' the contents of these works varied wildly and those that survive are often poorly cataloged. Since the maps in these composite works were not intended to be compatible with one another, bookbinders had to go to sometimes extreme lengths to combine them: pasting smaller maps down to larger sheets which were then stitched into the books, larger maps trimmed close and then folded to fit smaller bindings. We have also encountered some maps, usually found separately, yet printed to the same sheets to be included together in bound works.The popularity of these works, and their utility, appear to have influenced Ortelius in his project of creating the first true, uniform atlas in 1570. Despite the proliferation of Italian mapmakers in the 1560s and 70s, only a few lived beyond the Italian plagues of 1575-77, and these survivors seem to have prospered mainly by their acquisition of plates engraved prior to those plagues. The absence of any Italian response to Ortelius' work is more likely to have been a product of the devastation wrought by the pestilence than any overwhelming superiority of the Flemish work.
Publication History and Census
This map was engraved by Nicolo Nelli on behalf of Bertelli, who sold the map both as a separate issue and included it in his atlases factice. The map is consequently quite rare: only four examples are cataloged in institutional collections, at the Newberry Library, the British Library, the Bayerische Staatsbibliothek, and the Bibliotheque Nationale de France.CartographerS
Ferrando Bertelli (c. 1525 - 1572) was an Italian engraver, living and working in Venice in the middle part of the sixteenth century. He is among the mot prolific of the map engravers collectively referred to as 'Lafreri School' mapmakers, whose elegant, rare, and distinctive maps are now among the most sought-after by collectors. Nothing is known of his education or training; he produced composite atlases in conjunction with Camocio, Forlani and Zenoi. His death in 1572 was almost certainly due to Venice's struggle with the plague, which appears to have disproportionately punished that city's printing trade. More by this mapmaker...
Giacomo Gastaldi (c. 1500 - October, 1566) was an Italian astronomer, cartographer, and engineer active in the second half of the 16th century. Gastaldi (sometimes referred to as Jacopo or Iacobo) began his career as an engineer, serving the Venetian Republic in that capacity until the fourth decade of the sixteenth century. During this time he traveled extensively, building a large library relating to voyages and exploration. From about 1544 he turned his attention to mapmaking, working extensively with Gextantiovanni Battista Ramusio, Nicolo Bascarini, and Giovanbattista Pedrezano, as well as taking private commissions for, among others, Venice's Council of Ten. He is credited with the fresco maps of Asia and Africa still extant in the map room of the Doge's Palace. Gastaldi was also one of the first cartographers to embrace copper plate over woodblock engraving, marking an important development in the history of cartography. His 1548 edition of Ptolemy's Geographia was the first to be printed in a vernacular; it was the first to be printed in copperplate. As with his Swiss/German contemporary Münster, Gastaldi's work contained many maps depicting newly discovered regions for the first time, including the first map to focus on the East Coast of North America, and the first modern map of the Indian Peninsula. His works provided the source for the vast majority of the Venetian and Roman map publishers of the 1560s and 70s, and would continue to provide an outsize influence on the early maps of Ortelius, De Jode, and Mercator. Learn More...
Claudius Ptolemy (83 - 161 AD) is considered to be the father of cartography. A native of Alexandria living at the height of the Roman Empire, Ptolemy was renowned as a student of Astronomy and Geography. His work as an astronomer, as published in his Almagest, held considerable influence over western thought until Isaac Newton. His cartographic influence remains to this day. Ptolemy was the first to introduce projection techniques and to publish an atlas, the Geographiae. Ptolemy based his geographical and historical information on the "Geographiae" of Strabo, the cartographic materials assembled by Marinus of Tyre, and contemporary accounts provided by the many traders and navigators passing through Alexandria. Ptolemy's Geographiae was a groundbreaking achievement far in advance of any known pre-existent cartography, not for any accuracy in its data, but in his method. His projection of a conic portion of the globe on a grid, and his meticulous tabulation of the known cities and geographical features of his world, allowed scholars for the first time to produce a mathematical model of the world's surface. In this, Ptolemy's work provided the foundation for all mapmaking to follow. His errors in the estimation of the size of the globe (more than twenty percent too small) resulted in Columbus's fateful expedition to India in 1492.
Ptolemy's text was lost to Western Europe in the middle ages, but survived in the Arab world and was passed along to the Greek world. Although the original text almost certainly did not include maps, the instructions contained in the text of Ptolemy's Geographiae allowed the execution of such maps. When vellum and paper books became available, manuscript examples of Ptolemy began to include maps. The earliest known manuscript Geographias survive from the fourteenth century; of Ptolemies that have come down to us today are based upon the manuscript editions produced in the mid 15th century by Donnus Nicolaus Germanus, who provided the basis for all but one of the printed fifteenth century editions of the work. Learn More...
Nicolò Nelli (1530-1572 or 1575) was a Venetian engraver and illustrator, remembered for his work on several maps and decorative title pages produced in the 1560s and 70s. Nothing is known of his education and training. No work of his postdates 1570, and he is thought to have been one of those in the Venetian printing trade lost to the plague that gripped the city between 1572 and 1575. Learn More...