This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
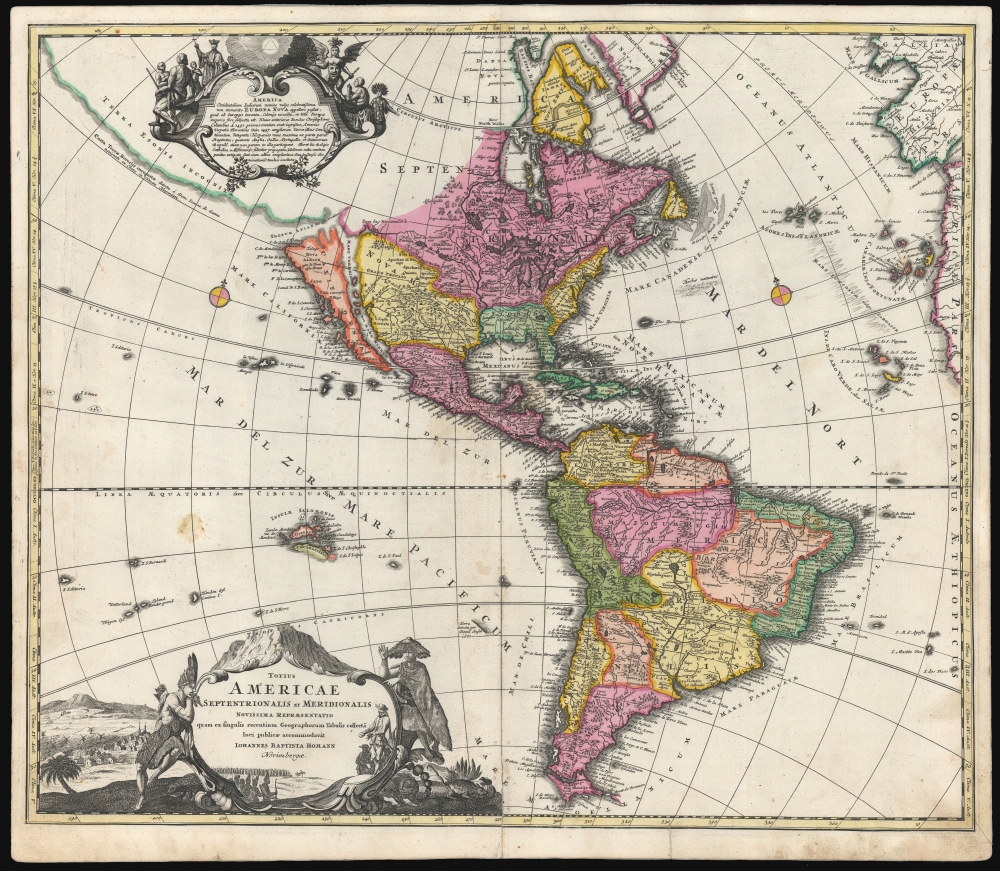
1707 / 1710 J. B. Homann Map of America (First Plate with California as an Island)
America-homann-1707
Title
1707 (undated) 19.25 x 22.5 in (48.895 x 57.15 cm) 1 : 39000000
Description
A Closer Look
In its generalities, the map evokes the Dutch maps of the previous century, featuring an insular California. Homann nonetheless incorporates significant detail from the state-of-the-art maps of the Parisian geographer Guillaume De l'Isle, most evidently in his depiction of the Great Lakes, the Mississippi, and the baffling Transmissississippi geography of Baron Lahontan. The illustration of the Sargasso Sea also derives from De l'Isle.The mapping of South America resembles in many respects that which appeared on the 1695 Sandrart Nova Tabula Americae, which Homann engraved. This work diverges from 17th-century maps of South America by its excision of Parime Lacus, a legendary lake in Guiana and the supposed location of El Dorado.
A Masterwork of Engraving
The decorative engraving is of a very high quality. The title cartouche - copied from the cartouche of Nicolas De Fer's 1699 L'Amerique, meridionale, et septentrionale - is flanked with native figures and contains a pastiche of seemingly conflicting images: European merchants offering wares to a multitude of Indian warriors, with a background of European-style towns replete with churches and windmills. The upper, descriptive cartouche features an allegory of missionary activity in America: to the left, a Jesuit proselytizes an attentive group of natives; but to the right, worshipful indigenes pray to a winged demon with a ravenous face in its belly. Surmounting the cartouche is a representation of the Trinity. While some of these features resemble the cartouche on the 1703 De l'Isle map of Canada, that can only be a partial source, and the two may stem from another unidentified original.Precursor of the Zurner America Map
It will be noted that the geographical features and typography of the present map also appear on Adam Friedrich Zurner's Americae tam Septentrionalis quam Meridionalis in Mappa Geographica Delineatio, printed by Pieter Schenk. The Zurner was added in 1709 in Schenk's Atlas Contractus, and was almost certainly copied from this map.Publication History and Census
The present example was included in a 1710 edition of Homann's Neuer Atlas. We see examples in institutional collections cataloged with dates as early as 1700, but given the content of the map, these dates are not credible. We see no examples of Homann's Neuer Atlas earlier than 1707; thus, the present work is an early printing of the map. This example, without a privilege and with California as an island, is the first plate of the map. We see this plate appearing in Homann atlases as late as 1716, and some later examples may have been produced. Most examples appearing on the market are of the later, post-privilege plate, entirely re-engraved by Homann's son Johann Christoph. The separate map in its later printings is well represented in institutional collections and appears on the market from time to time. This first plate appears much less frequently, although past poor cataloging of Homann maps foils close analysis.CartographerS
Johann Baptist Homann (March 20, 1664 - July 1, 1724) was the most prominent and prolific map publisher of the 18th century. Homann was born in Oberkammlach, a small town near Kammlach, Bavaria, Germany. As a young man, Homann studied in a Jesuit school and nursed ambitions of becoming a Dominican priest. Nonetheless, he converted to Protestantism in 1687, when he was 23. It is not clear where he mastered engraving, but we believe it may have been in Amsterdam. Homann's earliest work we have identified is about 1689, and already exhibits a high degree of mastery. Around 1691, Homann moved to Nuremberg and registered as a notary. By this time, he was already making maps, and very good ones at that. He produced a map of the environs of Nürnberg in 1691/92, which suggests he was already a master engraver. Around 1693, Homann briefly relocated to Vienna, where he lived and studied printing and copper plate engraving until 1695. Until 1702, he worked in Nuremberg in the map trade under Jacob von Sandrart (1630 - 1708) and then David Funck (1642 - 1709). Afterward, he returned to Nuremberg, where, in 1702, he founded the commercial publishing firm that would bear his name. In the next five years, Homann produced hundreds of maps and developed a distinctive style characterized by heavy, detailed engraving, elaborate allegorical cartouche work, and vivid hand color. Due to the lower cost of printing in Germany, the Homann firm could undercut the dominant French and Dutch publishing houses while matching their diversity and quality. Despite copious output, Homann did not release his first major atlas until the 33-map Neuer Atlas of 1707, followed by a 60-map edition of 1710. By 1715, Homann's rising star caught the attention of the Holy Roman Emperor Charles VI, who appointed him Imperial Cartographer. In the same year, he was also appointed a member of the Royal Academy of Sciences in Berlin. Homann's prestigious title came with several significant advantages, including access to the most up-to-date cartographic information as well as the 'Privilege'. The Privilege was a type of early copyright offered to very few by the Holy Roman Emperor. Though less sophisticated than modern copyright legislation, the Privilege offered limited protection for several years. Most all J. B. Homann maps printed between 1715 and 1730 bear the inscription 'Cum Priviligio' or some variation. Following Homann's death in 1724, the firm's map plates and management passed to his son, Johann Christoph Homann (1703 - 1730). J. C. Homann, perhaps realizing that he would not long survive his father, stipulated in his will that the company would be inherited by his two head managers, Johann Georg Ebersberger (1695 - 1760) and Johann Michael Franz (1700 - 1761), and that it would publish only under the name 'Homann Heirs'. This designation, in various forms (Homannsche Heirs, Heritiers de Homann, Lat Homannianos Herod, Homannschen Erben, etc.) appears on maps from about 1731 onwards. The firm continued to publish maps in ever-diminishing quantities until the death of its last owner, Christoph Franz Fembo (1781 - 1848). More by this mapmaker...
Guillaume De l’Isle (1675 - 1726) was a French cartographer, and arguably the finest mapmaker at the beginning of the eighteenth century. He was the son of Claude De L'Isle (1644 -1720), a Paris-based historian and geographer under Nicholas Sanson, then the leading light of French cartography. He was the chief proponent of the school of 'positive geography' and the primary figure defining the heights of the Golden Age of French Cartography. Guillaume's skill as a cartographer was so prodigious that he drew his first map at just nine years of age. He was tutored by J. D. Cassini in astronomy, science, mathematics and cartography. By applying these diverse disciplines to the vast stores of information provided by 18th century navigators, Guillaume created the technique that came to be known as 'scientific cartography', essentially an extension of Sanson's 'positive geography'. This revolutionary approach transformed the field of cartography and created a more accurate picture of the world. Among Guillaume's many firsts are the first naming of Texas, the first correct map of the Mississippi, the final rejection of the insular California fallacy, and the first identification of the correct longitudes of America. Stylistically De L'Isle also initiated important changes to the medium, eschewing the flamboyant Dutch style of the previous century in favor of a highly detailed yet still decorative approach that yielded map both beautiful and informative. Guillaume was elected to the French Academie Royale des Sciences at 27. Later, in 1718, he was also appointed 'Premier Geographe du Roi', an office created especially for him. De L'Isle personally financed the publication of most of his maps, hoping to make heavy royalties on their sales. Unfortunately he met an untimely death in 1728, leaving considerable debt and an impoverished child and widow. De L'Isle's publishing firm was taken over by his assistant, Phillipe Buache, who would also become his son in law. Learn More...