This item below is out of stock, but another example (left) is available. To view the available item, click "Details."
Details
1630 / 1640 Blaeu Map of Asia: Superb Original Color
$5,000.00
1630 / 1635 Blaeu Map of Asia: An Original Color Example
Asia-blaeu-1630
Title
1630 (undated) 16 x 22 in (40.64 x 55.88 cm) 1 : 20000000
Description
The Map
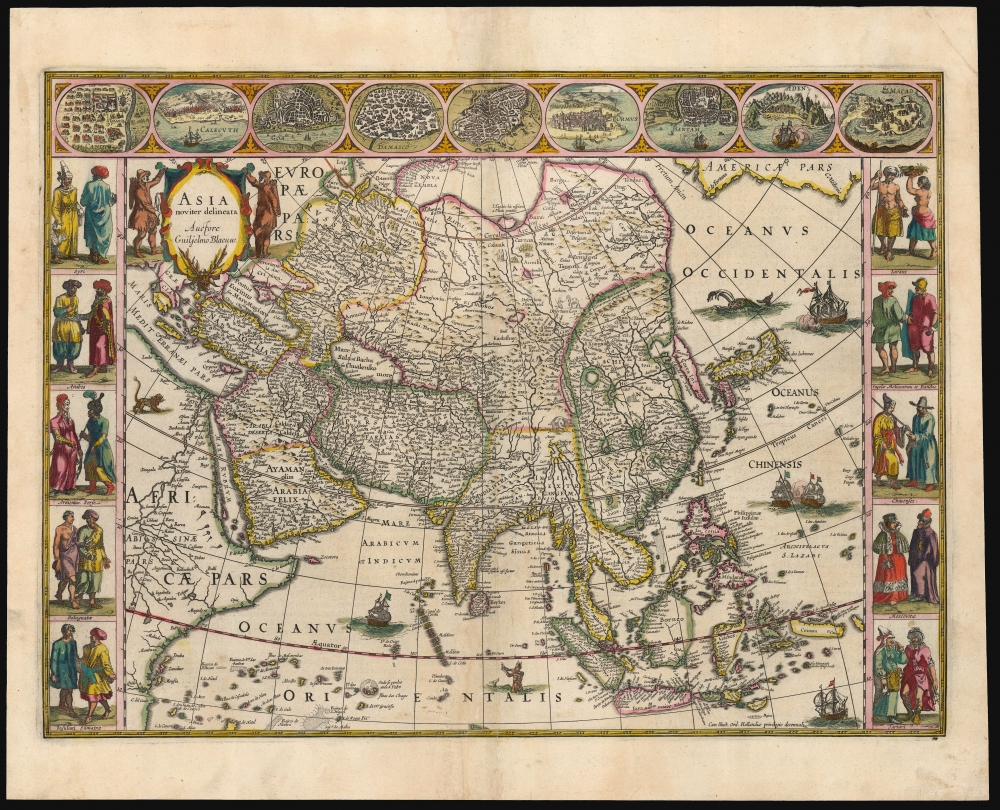
Blaeu's map is essentially a reduced version of his own 1608 wall map of the continent, which would provide the standard for virtually all mapping of Asia until the last quarter of the 17th century. Blaeu's atlas map here, first engraved in 1617, is particularly prized for its clarity and sharpness, presenting copious detail (and its many decorative features) without sacrificing legibility. The coastline, in particular, is rich in toponomy and the overall shape of the continent is remarkably accurate. Points within the continent, nonetheless, reveal the European ignorance of Asia's interior that would maintain into the second half of the century. For example, the Caspian Sea is presented here spanning further east-to-west than the actual north-to-south, an error typical of the 16th century maps of the continent. Japan and Korea are shown after the Portuguese model first published in the 1580s by Ortelius - with Hokkaido nowhere to be seen, and with Korea as a slender island.The Cities
Along the top border of the map are nine medallions containing views of Asian cities of importance. The Sri Lankan entrepot of Candy and the southwestern Indian ports of Calicut and Goa; Damascus and Jerusalem in the Levant; the Arabian port of Aden; Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf and the spice ports of Bantam and Macao are depicted here. These emphasize not only the religious focus of the near East, but also the key trade cities that were fueling the Dutch ascendency that both created maps like this, as well as the demand for them. Blaeu's source for these views was the Braun and Hogenberg Civitates Orbis Terrarum, the first printed 'city atlas' or collection of city plans and views from all over the explored world.Cartes à Figures
During the Dutch Golden Age of mapmaking in the first half of the 17th century, maps' decorative elements reached a height that would be alluded to but seldom matched in later periods of cartography. 'Cartes à Figures,' that is to say maps with human figures in decorative borders, were at the pinnacle of Dutch decorative cartography. These decorations were not without purpose. Atlas maps of the day were not meant to guide the prospective traveler, but were intended to inform the literate layperson what the rest of the world was like. The upper decorative border of this map with its city plans and views communicates how the denizens of Asia live: the border decoration on the left and right are meant to show what the denizens of Asia look and dress like. Typically, these pair a man and a woman for each region. Blaeu's Asia features Syrians, Arabians, Persians, Filipinos and Sumatrans; Javans, Moluccans, Chinese, Russians and Tatars.Cartes à figures were deluxe productions and seldom produced for narrow, regional maps save in scarce separate issues, and not all mapmakers included them in regular atlases. Willem Blaeu's world and continental maps are considered classics of the form.
Publication History and Census
This map was first engraved in 1617 and offered as a separate issue. This first state (the 1617 separate issue) can be distinguished by the author's imprint, 'Auctore Guil. Janssonio.' Atlas editions - such as this example - show the name changed to reflect Blaeu's use of his father's nickname (Blaeu,) a move the mapmaker made to better distinguish himself from his competitor, Jan Jansson. Such examples first appeared in Blaeu's 1630 Appendix; thereafter the map would be included in Blaeu's atlases in which it would remain until the end of the company's existence in 1672. At some point the plate developed a crack near the centerfold; the present example shows no evidence of this having yet occurred, and so this is a second state example of the map. No printings later than 1670 are known, indicating that the copperplate was among those destroyed in the great fire that finished the company. The present example conforms typographically to examples found in the 1635 Le Théâtre du Monde, the first French-text edition of the Blaeu Atlas. The map and its atlas are well represented in institutional collections in its many editions. Examples with original color of this quality and condition have grown scarce.Cartographer
Willem Janszoon Blaeu (1571 - October 18, 1638), also known as Guillaume Blaeu and Guiljelmus Janssonius Caesius, was a Dutch cartographer, globemaker, and astronomer active in Amsterdam during the late 16th and early 17th centuries. Blaeu was born 'Willem Janszoon' in Alkmaar, North Holland to a prosperous herring packing and trading family of Dutch Reformist faith. As a young man, he was sent to Amsterdam to apprentice in the family business, but he found the herring trade dull and instead worked for his cousin 'Hooft' as a carpenter and clerk. In 1595, he traveled to the small Swedish island of Hven to study astronomy under the Danish Enlightenment polymath Tycho Brahe. For six months he studied astronomy, cartography, instrument making, globe making, and geodesy. He returned to Alkmaar in 1596 to marry and for the birth of his first son, Johannes (Joan) Blaeu (1596 – 1673). Shortly thereafter, in 1598 or 1599, he relocated his family to Amsterdam where he founded the a firm as globe and instrument makers. Many of his earliest imprints, from roughly form 1599 - 1633, bear the imprint 'Guiljelmus Janssonius Caesius' or simply 'G: Jansonius'. In 1613, Johannes Janssonius, also a mapmaker, married Elizabeth Hondius, the daughter of Willem's primary competitor Jodocus Hondius the Elder, and moved to the same neighborhood. This led to considerable confusion and may have spurred Willam Janszoon to adopt the 'Blaeu' patronym. All maps after 1633 bear the Guiljelmus Blaeu imprint. Around this time, he also began issuing separate issue nautical charts and wall maps – which as we see from Vermeer's paintings were popular with Dutch merchants as decorative items – and invented the Dutch Printing Press. As a non-Calvinist Blaeu was a persona non grata to the ruling elite and so he partnered with Hessel Gerritsz to develop his business. In 1619, Blaeu arranged for Gerritsz to be appointed official cartographer to the VOC, an extremely lucrative position that that, in the slightly more liberal environment of the 1630s, he managed to see passed to his eldest son, Johannes. In 1633, he was also appointed official cartographer of the Dutch Republic. Blaeu's most significant work is his 1635 publication of the Theatrum orbis terrarum, sive, Atlas Novus, one of the greatest atlases of all time. He died three years later, in 1638, passing the Blaeu firm on to his two sons, Cornelius (1616 - 1648) and Johannes Blaeu (September 23, 1596 - December 21, 1673). Under his sons, the firm continued to prosper until the 1672 Great Fire of Amsterdam destroyed their offices and most of their printing plates. Willem's most enduring legacy was most likely the VOC contract, which ultimately passed to Johannes' son, Johannes II, who held the position until 1617. As a hobbyist astronomer, Blaeu discovered the star now known as P. Cygni. More by this mapmaker...