This item below is out of stock, but another example (left) is available. To view the available item, click "Details."
Details
1550 / 1574 Munster Map of Asia
$2,000.00
1578 Munster Map of Asia
Asia-munster-1540
Title
1540 (undated) 10.5 x 13.5 in (26.67 x 34.29 cm) 1 : 40000000
Description
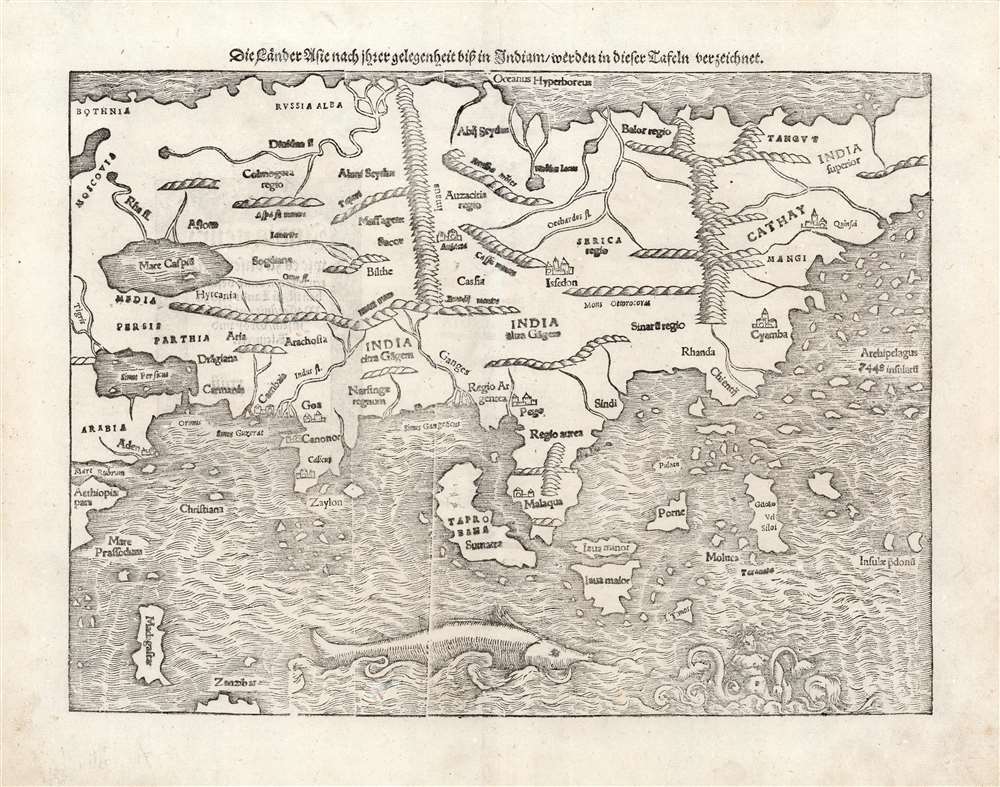
Southeast Asia and the East Indies
The Portuguese trading post of Malaqua in Southeast Asia is also present. Münster's depiction of Southeast Asia is recognizable, and surprisingly rich in novel information. Java - consistent with Marco Polo - is split in two, illustrated here as Java Major and Java Minor, and Münster retains Marco Polo's assertion of a vast archipelago in the Pacific made up of 7,448 islands. Münster's depiction of China (Cathay) is also consistent with Marco Polo's writings. At the northwestern angle of the Malay Peninsula, 'Pegu' can be found - the kingdom of the region now known as Myanmar. This first appeared on a printed map with the 1516 Martin Waldseemüller Carta Marina, which is how it would have come to Münster's attention. Drawing on Magellan's Voyage (1519 - 1522), he includes the Pacific 'Thieves' Islands' of Guam and Rota, here named 'Insular pdonū', acorrupted from Ladrones. Borneo appears as Porne. Predated only by Oronce Fine's world map, this map is the earliest to show any specific island of the Philippines: Palawan, here named Puloan. Likewise, this map gave its readers their first glimpse of the Spice Islands of the Moluccas and Gilolo. Although Münster extends Asia beyond the eastern limits of the page, his map of the Western Hemisphere would make clear that he intended to illustrate Asia and America as separate continents - as indeed his map of the world of the same era indicates.Asia in a Navigable World
Although this map does not name it, Münster's depiction of Asia is the first to be produced on the assumption that the body of water lying to the east was an ocean distinct from the Atlantic. His maps of the World and the Western Hemisphere are the first to name the Pacific. This map of Asia is the first to be produced consistent with that knowledge.Publication History and Census
This map was introduced in the first 1540 edition of Münster's Geographia. It remained in each edition of that work, and was included in all editions of Münster's Cosmographia until 1578, after which the double-page maps of the long-lived work were replaced and updated. German editions of Cosmographia are well represented in institutional collections. The separate map appears frequently in OCLC, although no examples of this 1578 state appears there.CartographerS
Sebastian Münster (January 20, 1488 - May 26, 1552), was a German cartographer, cosmographer, Hebrew scholar and humanist. He was born at Ingelheim near Mainz, the son of Andreas Munster. He completed his studies at the Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen in 1518, after which he was appointed to the University of Basel in 1527. As Professor of Hebrew, he edited the Hebrew Bible, accompanied by a Latin translation. In 1540 he published a Latin edition of Ptolemy's Geographia, which presented the ancient cartographer's 2nd century geographical data supplemented systematically with maps of the modern world. This was followed by what can be considered his principal work, the Cosmographia. First issued in 1544, this was the earliest German description of the modern world. It would become the go-to book for any literate layperson who wished to know about anywhere that was further than a day's journey from home. In preparation for his work on Cosmographia, Münster reached out to humanists around Europe and especially within the Holy Roman Empire, enlisting colleagues to provide him with up-to-date maps and views of their countries and cities, with the result that the book contains a disproportionate number of maps providing the first modern depictions of the areas they depict. Münster, as a religious man, was not producing a travel guide. Just as his work in ancient languages was intended to provide his students with as direct a connection as possible to scriptural revelation, his object in producing Cosmographia was to provide the reader with a description of all of creation: a further means of gaining revelation. The book, unsurprisingly, proved popular and was reissued in numerous editions and languages including Latin, French, Italian, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Münster's death of the plague in 1552. Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century, passing through 24 editions between 1544 and 1628. This success was due in part to its fascinating woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). Münster's work was highly influential in reviving classical geography in 16th century Europe, and providing the intellectual foundations for the production of later compilations of cartographic work, such as Ortelius' Theatrum Orbis Terrarum Münster's output includes a small format 1536 map of Europe; the 1532 Grynaeus map of the world is also attributed to him. His non-geographical output includes Dictionarium trilingue in Latin, Greek, and Hebrew, and his 1537 Hebrew Gospel of Matthew. Most of Munster's work was published by his stepson, Heinrich Petri (Henricus Petrus), and his son Sebastian Henric Petri. More by this mapmaker...
Heinrich Petri (1508 - 1579) and his son Sebastian Henric Petri (1545 – 1627) were printers based in Basel, Switzerland. Heinrich was the son of the printer Adam Petri and Anna Selber. After Adam died in 1527, Anna married the humanist and geographer Sebastian Münster - one of Adam's collaborators. Sebastian contracted his stepson, Henricus Petri (Petrus), to print editions of his wildly popular Cosmographia. Later Petri, brought his son, Sebastian Henric Petri, into the family business. Their firm was known as the Officina Henricpetrina. In addition to the Cosmographia, they also published a number of other seminal works including the 1566 second edition of Nicolaus Copernicus's De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium and Georg Joachim Rheticus's Narratio. Learn More...
Source
Munster's methodology in Cosmographia is notable in particular for his dedication to providing his readers with direct access to firsthand reports of his subjects wherever possible. Many of the maps were the result of his own surveys; others, the fruit of an indefatigable letter writing campaign to scholars, churchmen and princes throughout Europe, amicably badgering them for maps, views, and detailed descriptions of their lands. For lands further afield than his letters could reach, Munster relied on the best that the authorities of northern European scholarship could offer: he was well familiar with the work of Waldseemuller and other geographers of the early 16th century, and was well connected with the best geographers of his own generation. A disproportionate number of the maps of Cosmographia show contemporary geographical knowledge of the their respective areas for the very first time: The first map to show the continents of the Western Hemisphere; the first map to focus on the continent of Asia; the first modern map to name the Pacific Ocean; the first map to use a key; the first modern map of the British Isles and so on. Even in cases where earlier maps exist, Munster's works very often remain the earliest such acquirable by the collector.