This item below is out of stock, but another example (left) is available. To view the available item, click "Details."
Details
1826 Weiland Map of Turkey and Asia Minor
1826 (dated) $250.00
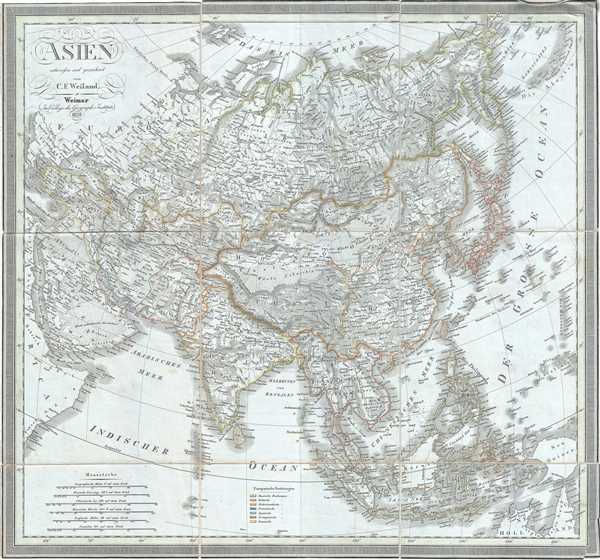
1828 Weiland Map of Asia
Asien-weiland-1828
Title
1828 (dated) 21 x 23 in (53.34 x 58.42 cm) 1 : 20000000
Description
During this time in Russia, around 1825, Russian army officers, called the Decembrists, protested against Nicholas I's ascension to the throne. They were however defeated and some were exiled to Siberia. There, against all odds, the Decembrists thrived making significant contributions to the cultural and economic growth of Siberia. In 1856, when the Decembrists received amnesty, only some returned to European Russia.
In the early 19th century Asia was coming under increasingly imperial European sway. In India, full British rule allowed England to attain naval and trade supremacy throughout the Eastern Hemisphere. Using India as a springboard, the English traded wool and Indian cotton for Chinese tea and textiles. By the 1830s, oversaturation of the Chinese market slackened Chinese demand for most British products. To make up for the trade deficit, British merchants introduced Indian opium to Chinese markets. Addictive and cheap, Opium became Britain's most profitable and important crop in world markets, pouring into China faster than tea poured into Britain. Opium addiction and its attendant social ills reached such catastrophic levels that the Chinese government took action and destroyed British opium in Canton. As this threatened English commercial interests, the crown responded, sparking the Opium Wars of 1839-1842. The superior British forces took complete control of Canton, occupied Shanghai, and blockaded Chinese ports, forcing the Chinese to sign the 1842 Treaty of Nanking. This unequal treaty (the first of many between European powers and China) granted Britain extensive trading rights in China.
This map was created by C. F. Weiland and published by the Weimar Geographical Institute.
CartographerS
Carl Ferdinand Weiland (1782 - 1847) was a German cartographer active with the Weimar Geographisches Institut, where he headed up map and globe production, in early and middle part of the 19th century. Weiland was a trained as a military cartographer who, with his career at the Geographisches Institut, move into the private market. Among his other work, Weiland issued a German edition of Carey and Lea's American Atlas. Their edition, which was fully re-engraved in Germany, is of superior workmanship and stands out as some of the finest 19th century maps of individual U.S. states printed outside of America.Carl Ferdinand Weiland (1782 - 1847) was a German cartographer active with the Weimar Geographisches Institut, where he headed up map and globe production, in early and middle part of the 19th century. Weiland was a trained as a military cartographer who, with his career at the Geographisches Institut, move into the private market. Among his other work, Weiland issued a German edition of Carey and Lea's American Atlas. Their edition, which was fully re-engraved in Germany, is of superior workmanship and stands out as some of the finest 19th century maps of individual U.S. states printed outside of America. More by this mapmaker...
Geographisches Institut, Weimar (fl. 1804 - c. 1903) was a German map and globe publishing house and geographical research institute based in Weimar. The organization primarily focused on republishing and improving upon the works of earlier cartographers, including Kitchin, Jefferys, Carey, and others. In general, its publications are known for their fine engraving, attention to detail, historical accuracy, and overall high quality. The firm was founded in 1804 by Friedrich Justin Bertuch (???? - c. 1845) and, on his death, passed to his son Robert Froreip (???? - 1855), then to Louis Denicks of Luneberg, then in 1859 to Voigt & Günther, in 1883 to F. Arnd, from 1890 - 1893 to Julius Kettler, and in 1903 to Max Wedekind. During the institute's height in the early 19th century, most of its cartographic publication was overseen by Carl Ferdinand Weiland (1782 - 1847). The firm also employed the cartographers Franz Xaver von Zach, Adam Christian Gaspari, Heinrich Kiepert, Karl (or Carl) and Adolf Graef, Julius Kettler, Carl Riemer and Karl Christian Bruhns. Weimar was a logical place for a collective like the Geographisches Institut to arise; it was a cultural mecca in the German-speaking world in the late 18th and 19th centuries because of its liberal atmosphere and associations with figures like Schiller, Herder, and, above all, Goethe, who spent most of his adult life in the city. Learn More...