This item below is out of stock, but another example (left) is available. To view the available item, click "Details."
Details
1772 Vaugondy / Diderot Map of Alaska, the Pacific Northwest and the Northwest Passage
$500.00
1772 Vaugondy / Diderot Map of Alaska, the Pacific Northwest and the Northwest Passage
DeFonte-vaugondy-1768-3
Title
1768 (dated) 11.5 x 14 in (29.21 x 35.56 cm) 1 : 19000000
Description
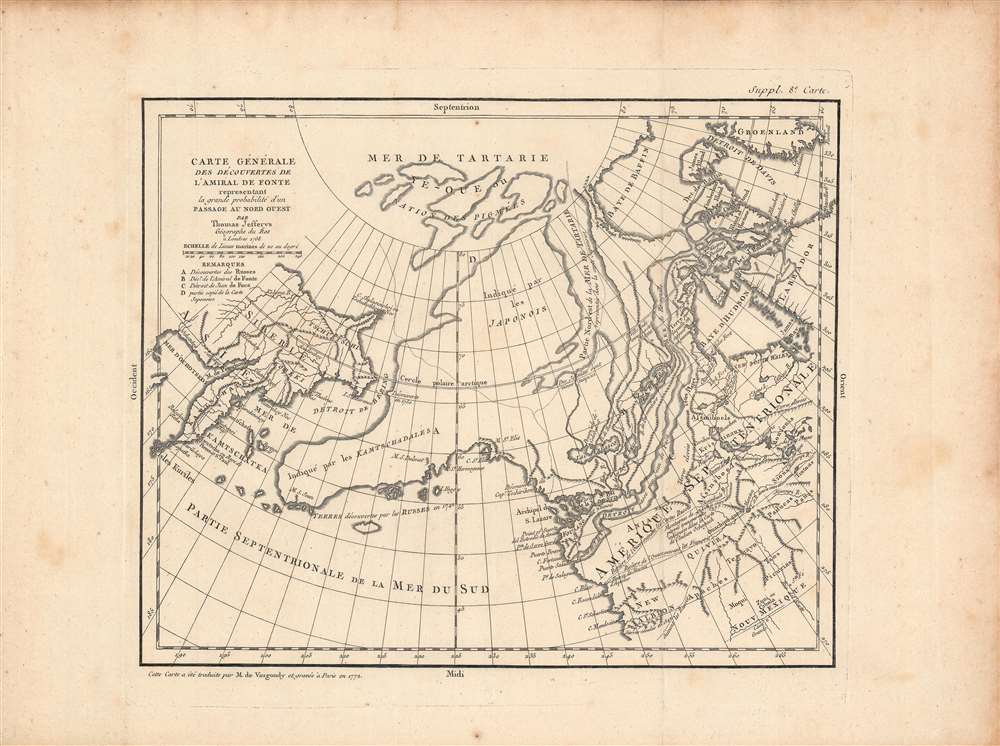
De Fonte
Barthlomew de Fonte was supposedly a Spanish Admiral who, sailing up the Pacific coast c. 1640, discovered a series of gigantic lakes, seas, and rivers heading eastward towards the Hudson Bay. Purportedly, upon one of these great inland lakes, he met with a ship from Boston that claimed to have come through a Northwestern Passage. De Fonte's story appeared in a short-lived 1706 English publication entitled 'Memoirs of the Curious.'The story inspired Joseph-Nicholas de l'Isle, younger brother of the better-known Guillaume de l'Isle, who at the time was employed by the Russian Tzar Peter the Great in the compilation of Russian surveys and discoveries in Siberia and the extreme northeast of Asia. When he published his somewhat accurate map of northeast Asia, the younger De l'Isle's paradoxically decided to include with it an entirely speculative map of North America based largely on De Fonte's letter. De l'Isle's mantle was later taken up by Jefferys, another ardent supporter of the Northwest Passage theory, in his own map of the region, which was, ultimately, the inspiration for this map by Vaugondy.
In accord with De Fonte's suggestions, this map displays the Strait of Juan de Fuca continuing inland past the large lakes of Velasco, Belle, and De Fonte to communicate with the Baffin and Hudson Bay. There are also a series of rivers and waterways connecting the lakes themselves to an outlet in the Arctic.
Based upon Russian reports, Robert de Vaugondy renamed the 'Straits of Anian,' the 'Detroit de Bering,' paying homage to the great Russian navigator. Anian itself has been moved southward nearer to the Strait of Juan de Fuca. Anian is a term derived from the journals of Marco Polo that first appeared cartographically in 1561 on a map by the Venetian cartographer Bolognini Zaltieri. Later it appeared in a John Donne poem, 'Anyan if I go west by the North-West passage.' However, it was interpreted as the Bering Strait by cartographers, successfully transitioning it from the realms of poetry to cartography. Anian presupposed the existence of a Northwest Passage and, as such, was entirely mythical, though the lands that are now Alaska long bore that name.
A Chinese Colony in North Ameica
Just next to Anian is 'Fousang des Chinois,' based on the Chinese legend of Fusang (扶桑), noted as a location far to the east of China. This idea was picked up by European scholars (early Orientalists/ Sinologists) such as Joseph de Guignes, a contemporary of de Vaugondy, who theorized that Fou-sang ought to be located on the west coast of North AmericaKingdoms of Gold
Further south still we find Quivira, one of the legendary northern American Kingdoms of Gold. Nearer to Russia the Aleutian Islands have been consolidated into a large peninsular landmass extending eastward towards Asia. In the extreme north, between 80 and 60 degrees of latitude, is an archipelago, presumably discovered by the Japanese, and purportedly inhabited entirely by pigmies.Intellectual Debate
This entire map is in sharp contrast to De l'Isle map of the same region. In an alternative to the Jefferys map, De l'Isle imagined a slightly more distorted picture of the extreme northwest divided into several great islands with gigantic bays and inland seas heading eastward towards Hudson Bay. These two disparate cartographic interpretations of the De Fonte story inspired considerable debate among European intellectual circles until the matter was finally put to rest by the expeditions of James Cook. Nonetheless, this is an altogether fascinating map of the Northwest Passage and the American West, a must for any serious collection dedicated to this region.Publication History and Census
This map was translated by Robert de Vaugondy in 1772, based on Thomas Jefferys' 1768 original. It was part of the ten-map series prepared by Vaugondy for the Supplement to Diderot's Encyclopédie, of which this is plate 8. This seminal map series, exploring the mapping of North American and specifically the Northwest Passage, was one of the first studies in comparative cartography.CartographerS
Robert de Vaugondy (fl. c. 1716 - 1786) was French may publishing from run by brothers Gilles (1688 - 1766) and Didier (c. 1723 - 1786) Robert de Vaugondy. They were map publishers, engravers, and cartographers active in Paris during the mid-18th century. The father and son team were the inheritors to the important Nicolas Sanson (1600 - 1667) cartographic firm whose stock supplied much of their initial material. Graduating from Sanson's maps, Gilles, and more particularly Didier, began to produce their own substantial corpus. The Vaugondys were well-respected for the detail and accuracy of their maps, for which they capitalized on the resources of 18th-century Paris to compile the most accurate and fantasy-free maps possible. The Vaugondys compiled each map based on their own geographic knowledge, scholarly research, journals of contemporary explorers and missionaries, and direct astronomical observation. Moreover, unlike many cartographers of this period, they took pains to reference their sources. Nevertheless, even in 18th-century Paris, geographical knowledge was limited - especially regarding those unexplored portions of the world, including the poles, the Pacific Northwest of America, and the interiors of Africa, Australia, and South America. In these areas, the Vaugondys, like their rivals De L'Isle and Buache, must be considered speculative or positivist geographers. Speculative geography was a genre of mapmaking that evolved in Europe, particularly Paris, in the middle to late 18th century. Cartographers in this genre would fill in unknown lands with theories based on their knowledge of cartography, personal geographical theories, and often dubious primary source material gathered by explorers. This approach, which attempted to use the known to validate the unknown, naturally engendered rivalries. Vaugondy's feuds with other cartographers, most specifically Phillipe Buache, resulted in numerous conflicting papers presented before the Academie des Sciences, of which both were members. The era of speculative cartography effectively ended with the late 18th-century explorations of Captain Cook, Jean Francois de Galaup de La Perouse, and George Vancouver. After Didier died, his maps were acquired by Jean-Baptiste Fortin, who in 1787 sold them to Charles-François Delamarche (1740 - 1817). While Delamarche prospered from the Vaugondy maps, he defrauded Vaugondy's window Marie Louise Rosalie Dangy of her rightful inheritance and may even have killed her. More by this mapmaker...
Denis Diderot (October 5, 1713 - July 31, 1784) was a French Enlightenment era philosopher, publisher and writer. Diderot was born in the city of Langres, France and educated at the Lycée Louis le Grand where, in 1732, he earned a master of arts degree in philosophy. Diderot briefly considered careers in the clergy and in law, but in the end chose the more fiscally challenge course of a writer. Though well respected in philosophical circles Diderot was unable to obtain any of the government commissions that commonly supported his set and consequently spent much of his life in deep poverty. He is best known for his role in editing and producing the Encyclopédie . The Encyclopédie was one of the most revolutionary and impressive works of its time. Initially commissioned as a translation of Ephraim Chambers' Cyclopaedia, or Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences, Diderot instead turned into a much larger and entirely new work of monumental depth and scope. Diderot's Encyclopédie was intended to lay bare before the common man the intellectual mysteries of science, art and philosophy. This revolutionary mission was strongly opposed by the powers of the time who considered a learned middle class it a threat to their authority. In the course of the Encyclopédie production Diderot was imprisoned twice and the work itself was officially banned. Nonetheless, publication continued in response to a demand exceeding 4000 subscribers. The Encyclopédie was finally published in 1772 in 27 volumes. Following the publication of the Encyclopédie Diderot grew in fame but not in wealth. When the time came to dower his only surviving daughter, Angelique, Diderot could find no recourse save to sell his treasured library. In a move of largess, Catherine the II Russia sent an emissary to purchased the entire library on the condition that Diderot retain it in his possession and act as her "librarian" until she required it. When Diderot died of gastro-intestinal problems 1784, his heirs promptly sent his vast library to Catherine II who had it deposited at the Russian National Library, where it resides to this day. Learn More...
Thomas Jefferys (1695 - November 20, 1771) was one of the most prominent and prolific map publishers and engravers of his day. Jefferys was born in Birmingham and was apprenticed to the engraver Emmanuel Bowen in 1735. Later, in the 1740s he engraved several maps for the popular periodical Gentleman's Magazine. Around 1740 Jefferys was finally able to go into business for himself and in 1746 received an appointment as 'Geographer to Fredrick, Prince of Wales,' which shortly after translated to the position of 'Royal Cartographer to King George III.' Jefferys initially specialized in compiling and re-engraving the works of earlier cartographers into more coherent cartographic wholes. Later, while not salaried position, Jefferys' appointment as 'Royal Cartographer' guaranteed preferential access to the most up to date cartographic material available, allowing him to produce new and updated charts of exceptional accuracy. He his best known for his maps of the Americas, particularly the posthumously published 1775 American Atlas, which included some of the finest and most important late colonial era maps of America ever made. Despite his prolific publishing history, royal appointments, and international publishing fame, Jefferys lived most of his life in dire economic straits. He was bailed out of bankruptcy by Robert Sayer during the production of the American Atlas. In the end, Jefferys died suddenly with very little to his name. Nonetheless, his cartographic legacy survived, and even after his death in 1771, many of his important maps continued to be published and republished by Sayer and Bennet, Conrad Lotter, Georges Louis Le Rouge, Laurie and Whittle, and others. Many attribute some of Jefferys best maps to the colorful and criminally inclined Irish cartographic genius Braddock Mead (John Green, c. 1688 - 1757), who is considered the 'secret behind Jefferys.' Jefferys was succeeded by his son, also Thomas, who had little success as a cartographer and eventually partnered with, then sold his stock and plates to William Faden - Jefferys' true heir. Learn More...
Joseph-Nicolas De l'isle (April 4, 1688 – September 11, 1768) was a French astronomer and cartographer. He was the younger brother of the illustrious Geographer to the King, Guillaume De l'isle. He studied astronomy under Joseph Lieutaud and Jacques Cassini. In 1714 he entered the French Academy of Sciences; from 1719 to 1722 he was employed at the Royal observatory, and would meet Halley in 1724. In 1725 he was among the Western academics invited to Saint Petersburg by Tsar Peter the Great; his appointment to the Russian Academy would be both lucrative and academically to his profit, giving him access to the most current surveys of the easternmost reaches of the Russian Empire, including the revelations of Vitus Bering. He personally participated in expeditions to Siberia, with the object of studying astronomical events observations but also making cartographic, ethnographic and zoological observations. He was invited to collaborate with Ivan Kirilov on a planned atlas of the Russian Empire, but disagreements about methodology limited his engagement and the Atlas was abandoned at Kirilov's death in 1737. De l'Isle's extreme rigor, too proved to be frustratingly slow for the Academy, leading to his dismissal from the Atlas project in 1740. Accusations that he was sending secret documents to France surfaced as well. As De l'Isle's position grew increasingly untenable, he would request permission to leave Russia in 1743, which he would do in 1747. Ironically, the Atlas Rossicus would be published under De l'Isle's name; historians disagree whether the honor was justified. Upon his return to France, De l'Isle would vigorously publish maps containing the geographical data he gathered during his Russian tenure, to the extent that the accusations of his theft of secret Russian cartographic information appear credible. He would work extensively with his nephew-in-law, Philippe Buache, in publicizing an array of maps revealing the Russian discoveries in conjunction with an array of less credible cartographic revelations in the Pacific Northwest of America. Later, he would be instrumental in spurring the international effort to coordinate observations of the 1761 Transit of Venus, despite the execution of the observations being interfered with by the Seven Years' War. Learn More...