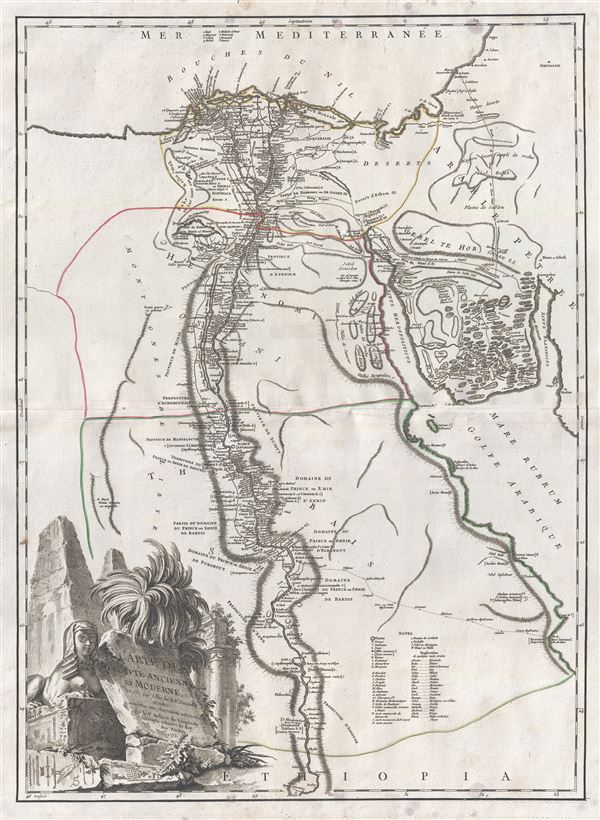
1753 Vaugondy Map of Egypt
Egypte-vaugondy-1757
Title
1753 (dated) 26 x 19.5 in (66.04 x 49.53 cm) 1 : 650000
Description
Possibly this map's most interesting aspect is its presentation of the ancient Lake Moeris (Lacus Moeris), now just a small lake called Birket Qarun and the legendary 'Labyrinth.' The lost Labyrinth was described by many classical authors including Herodotus, Strabo, Diodorus and Pliny. A sprawling megalithic complex designed by Imandes for the Pharaoh Amenemhet III, the Labyrinth is believed to have contained thousands of rooms filled with hieroglyphs and ancient Egyptian sculptures. Herodotus wrote about it in the fifth century B.C.:
Furthermore, they resolved to leave a memorial of themselves in common, and in pursuance of this resolve they made a labyrinth, a little above Lake Moeris, and situated near what is called the City of the Crocodiles. I saw it myself and it is indeed a wonder past words; for if one were to collect together all of the buildings of the Greeks and their most striking works of architecture, they would all clearly be shown to have cost less labor and money than this labyrinth. Yet the temple at Ephesus and that in Samos are surely remarkable. The pyramids, too, were greater than words can tell, and each of them is the equivalent of many of the great works of the Greeks; but the labyrinth surpasses the pyramids also. It has 12 roofed courts, with doors facing one another, 6 to the north and 6 to the south and in a continuous line. There are double sets of chambers in it, some underground and some above, and their number is 3,000; there are 1,500 of each. We ourselves saw the aboveground chambers, for we went through them so we can talk of them, but the underground chambers we can speak of only from hearsay. For the officials of the Egyptians entirely refused to show us these, saying that there were, in them, the coffins of the kings who had built the labyrinth at the beginning and also those of the holy crocodiles. So we speak from hearsay of these underground places; but what we saw aboveground was certainly greater than all human works. The passages through the rooms and the winding goings-in and out through the courts, in their extreme complication, caused us countless marvelings as we went through, from the court into the rooms, and from the rooms into the pillared corridors, and then from these corridors into other rooms again, and from the rooms into other courts afterwards. The roof of the whole is stone, as the walls are, and the walls are full of engraved figures, and each court is set round with pillars of white stone, very exactly fitted. At the corner where the labyrinth ends there is, nearby, a pyramid 240 feet high and engraved with great animals. The road to this is made underground.Several archeological surveys have been undertaken to unearth the labyrinth, but so far no findings have been confirmed.
Such was the labyrinth; but an even greater marvel is what is called Lake Moeris, beside which the labyrinth was built. The circuit of this lake is a distance of about 420 miles, which is equal to the whole seaboard of Egypt. The length of the lake is north and south, and its depth at the deepest is 50 fathoms [300 feet]. That it is handmade and dug, it itself is the best evidence. For in about the middle of the lake stand 2 pyramids that top the water, each one by 50 fathoms [300 feet], and each built as much again underwater; and on top of each there is a huge stone figure of a man sitting on a throne. So these pyramids are 100 fathoms [600 feet] high, and these 100 fathoms are the equivalent of a 600-foot furlong, the fathom measuring 6 feet, or four cubits (the cubit being six spans). The water in the lake is not fed with natural springs, for the country here is terribly waterless, but it enters the lake from the Nile by a channel; and for 6 months it flows into the lake, and then, another 6, it flows again into the Nile. During the 6 months that it flows out, it brings into the royal treasury each day a silver talent for the fish from it; and when the water flows in, it brings 20 minas a day.
A highly decorative title cartouche depicting a sphinx and pyramids appears in the bottom left quadrant. Drawn by Robert de Vaugondy and published in the 1757 issue of his Atlas Universal. The Atlas Universal was one of the first atlases based upon actual surveys. Therefore, this map is highly accurate (for the period) and has most contemporary town names correct, though historic names are, in many cases, incorrect or omitted.
Cartographer
Robert de Vaugondy (fl. c. 1716 - 1786) was French may publishing from run by brothers Gilles (1688 - 1766) and Didier (c. 1723 - 1786) Robert de Vaugondy. They were map publishers, engravers, and cartographers active in Paris during the mid-18th century. The father and son team were the inheritors to the important Nicolas Sanson (1600 - 1667) cartographic firm whose stock supplied much of their initial material. Graduating from Sanson's maps, Gilles, and more particularly Didier, began to produce their own substantial corpus. The Vaugondys were well-respected for the detail and accuracy of their maps, for which they capitalized on the resources of 18th-century Paris to compile the most accurate and fantasy-free maps possible. The Vaugondys compiled each map based on their own geographic knowledge, scholarly research, journals of contemporary explorers and missionaries, and direct astronomical observation. Moreover, unlike many cartographers of this period, they took pains to reference their sources. Nevertheless, even in 18th-century Paris, geographical knowledge was limited - especially regarding those unexplored portions of the world, including the poles, the Pacific Northwest of America, and the interiors of Africa, Australia, and South America. In these areas, the Vaugondys, like their rivals De L'Isle and Buache, must be considered speculative or positivist geographers. Speculative geography was a genre of mapmaking that evolved in Europe, particularly Paris, in the middle to late 18th century. Cartographers in this genre would fill in unknown lands with theories based on their knowledge of cartography, personal geographical theories, and often dubious primary source material gathered by explorers. This approach, which attempted to use the known to validate the unknown, naturally engendered rivalries. Vaugondy's feuds with other cartographers, most specifically Phillipe Buache, resulted in numerous conflicting papers presented before the Academie des Sciences, of which both were members. The era of speculative cartography effectively ended with the late 18th-century explorations of Captain Cook, Jean Francois de Galaup de La Perouse, and George Vancouver. After Didier died, his maps were acquired by Jean-Baptiste Fortin, who in 1787 sold them to Charles-François Delamarche (1740 - 1817). While Delamarche prospered from the Vaugondy maps, he defrauded Vaugondy's window Marie Louise Rosalie Dangy of her rightful inheritance and may even have killed her. More by this mapmaker...