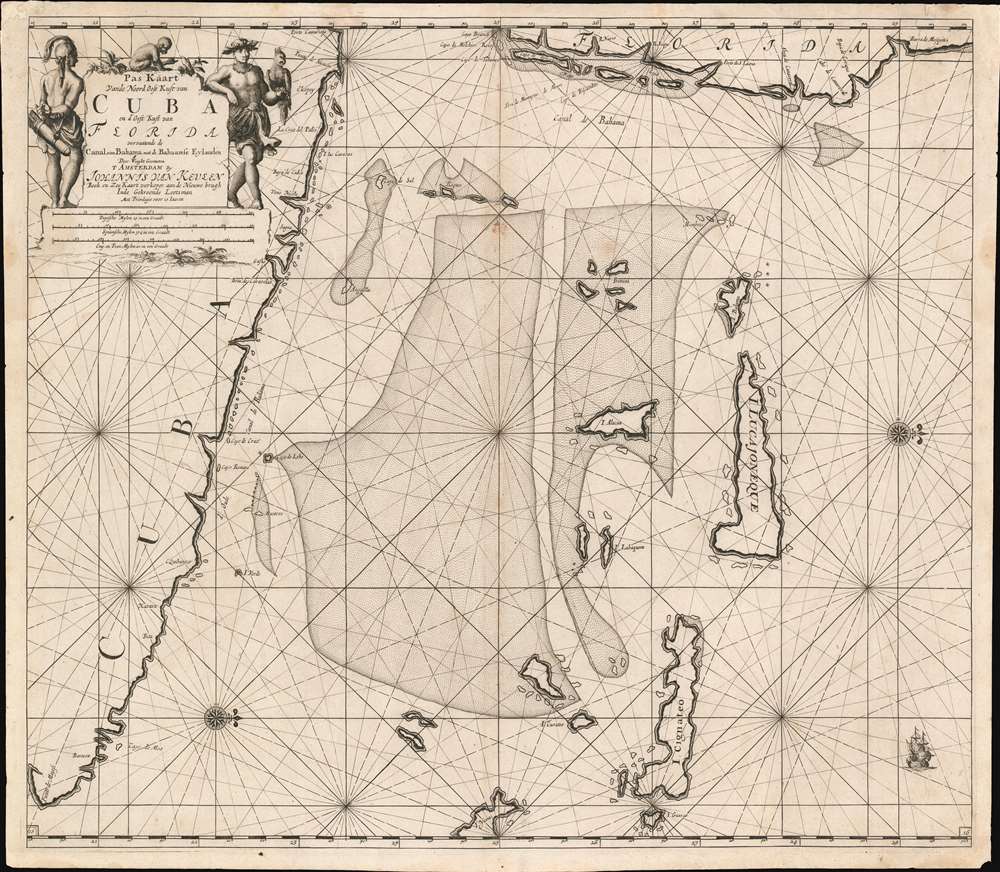
1695 Van Keulen Map of Florida, Cuba, and the Bahamas
FloridaCubaBahamas-vankeulen-1695
Title
1695 (undated) 20.25 x 23.25 in (51.435 x 59.055 cm) 1 : 1750000
Description
Sources
Cartographically Van Keulen derived this map from the 1675 map of Arend Roggeveen, Pascaerte Van 't Canael de Bahama as well as from Hessel Gerritsz's 1631 chart. The cartographic work of compiling this map is attributed in the title to Claes Jansz Vooght, a known partner in the Keulen firm.Golden Age of Caribbean Piracy (c. 1650 - 1730)
This map appeared at the height of the Golden Age of Caribbean Piracy (c. 1650 - 1730) and nowhere were pirates more likely to strike than in this narrow passage between Florida and the Bahamas. Dutch pirates operating with the support of the Dutch West India Company dominated the 17th century until the rise of English piracy in the 1690s. Roughly three years after this map was issued English (and many other) pirates began establishing themselves in the Bahamas, which were ideally situated to raid Spanish treasure galleons on en route from Havana to St. Augustine, their last stop in the New World before turning out to Sea for Europe. By early 1700s, Nassau had been declared a 'Pirate Republic' and more than 1,000 pirates had established themselves in the region. The inaccuracies of the charting of the Bahamas throughout this period highlight the attraction the archipelago held for pirates: the shallow, treacherous and labyrinthine waters made an admirable hiding place from which to raid the narrow, deeper waters off the Florida Coast.Publication History and Census
Van Keulen issued this map in three states, of which this is the third. The first state appeared in 1684 and is identifiable for its lack of page number. Subsequent states appeared in 1687, and c. 1695. This map was published in both Van Keulen's Zee-Fakkel and his Zee-Atlas, which were published congruently to about 1702. Only two examples of the chart, in different editions, appear in OCLC, although the atlases are reasonably well represented in institutional collections.CartographerS
Johannes Van Keulen (1654 – 1715) was a Dutch cartographer active in Amsterdam during the late 17th century. Van Keulen was the son of Lucas van Keulen. Van Keulen's firm, ‘In de Gekroonde Lootsman' (In the Crowned Pilot), was founded in 1678 and registered with the Amsterdam bookseller's guild as 'Cross staff-maker and bookseller.' (The cross-staff is a nautical instrument used to determine latitude.) Two years later, in 1680, they obtained a patent from the States General of Holland and West Friesland to publish nautical charts and atlases. Together with his partner, the cartographer Claes Janz Vooght, Van Keulen published numerous atlases and nautical charts, including the Zee Atlas and Nieuwe Lichtende Zee-Fakkel. It was a massive five-volume atlas containing more than 130 nautical charts. The Zee-Fakkel established the Van Keulen firm as the pre-eminent maker of Dutch sea charts in the late 17th and early 18th century. In 1714, one year before Johannes Van Keulen's death, his son, Gerard van Keulen (1678 - 1726), took charge. Gerard continued to update and republish the Zee-Fakkel until his own death in 1726. The firm was later passed on to Gerard's son, Johannes II Van Keulen (1704 - 1755), who significantly updated the atlas, especially with regard to Asia, issuing the 1753 4th Volume, known as the 'Secret Atlas'. The final editions of the atlas were published by Gerard Hulst van Keulen (1733 - 1801), Joannes II's son. The final true Van Keulen edition of the Zee-Fakkel was published posthumously in 1803. It is noteworthy that though ostensibly controlled by the Van Keulen men, it was the Van Keulen widows who maintained and managed the firm in the periods following their husbands' deaths. After the death of Gerard Hulst Van Keulen's son, Johannes Hulst Van Keulen, ownership of the family plates and business fell into the hands of the Swart family, who continued to publish until the company closed its doors 1885, ending a cartographic legacy spanning nearly 207 years. More by this mapmaker...
Claes Jansz Vooght (1638 – 1696) was a Dutch astronomer, mathematician, teacher, surveyor and cartographer active in Amsterdam during the 17th century. Vooght described himself as a 'surveyor and teacher of mathematics and the art of navigation' and published extensively on these subjects. His is known to have been a surveyor for the Council of Holland and co-authored several books with Rembrantsz Dirck van Nierop. Though little is known of Vooght's life, his most important cartographic work appeared in conjunction with the prominent Johannes Van Keulen firm, with whom he partnered in 1680. Vooght was responsible for creating and compiling most of the maps in Van Keulen's seminal Nieuwe Lichtende Zee-Fakkel, with many early editions bearing only his name. Learn More...
Source
Grandson, Johannes II van Keulen (1704 - 1755) expanded the atlas in 1753 with Volume VI, illustrating Asian waters. This was a revolutionary addition. For three generations the Van Keulen's were the official cartographers of the VOC (Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie / United Dutch East India Company). Until 1753, to protect their long-standing trade monopoly, the VOC jealously guarded their hydrographic data on East Asian waters, refusing the allow charts to be printed and requiring oaths of secrecy from the Van Keulens (and Bleaus before them). This led to dangerously inaccurate often contradictory charts. Thus, in 1744 Jan Harmenszoon de Marre (1696 - 1763), the VOC's Amsterdam Examiner, was instructed to work with van Keulen to publish compile, compare, and resolve the VOC's hoard of jealously guarded manuscript charts of East Asian waters. Johannes II and de Marre published the sixth volume of the Zee-Fakkel, focusing on Asian waters - if only for internal VOC use.
This was likely an attempt to consolidate and improve the general hydrography. Previously, VOC charts in manuscript were disseminated to ship captains on an as-needed basis, to be returned upon a voyage's completion. They were rarely compared or amended. A study of several VOC manuscript charts issued between 1720 and 1760 reveal striking disparities, likely resulting either from the charts being updated or copied from earlier less accurate charts. Such led to avoidable navigational and thus trade risks. A printed nautical atlas, whose hydrography was built upon the most recent and up-to-date charts, reassessed by the greatest chartmaker of the age, was a natural solution.
The new atlas, ostensibly an extension (Volume VI) of the existing commercially issued Nieuwe Lichtende Zee-Fakkel, was intended only for VOC use, and so became known as the 'Secret Atlas'. The printing run was extremely small, and access tightly controlled. VOC ship captains navigating to the Far East were given a copy on departure and expected to return it in good condition on return. Even so, the maps of the 'Secret Atlas' were disseminated, perhaps by the van Keulen's themselves. We note evidence of 'secret' Dutch hydrography in charts of the English Pilot as well as in other Dutch charts. Nonetheless, original maps from 'Secret' Zee-Fakkel volume VI remain of the utmost rarity.