1513 Waldseemuller / Ptolemy Map of India
India-waldseemuller-1513
Title
1513 (undated) 14.5 x 22.75 in (36.83 x 57.785 cm) 1 : 10000000
Description
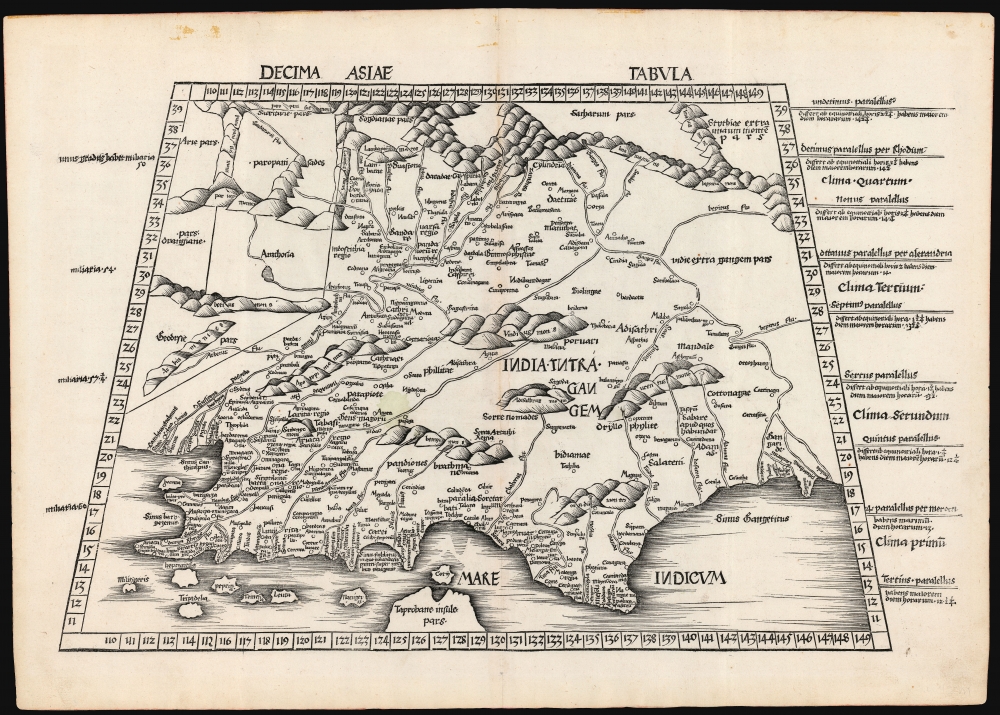
A Closer Look
This was Ptolemy's 10th map out of 12 covering Asia. It details the area between the Indus River and the Ganges, reaching from the Indian Ocean to the Imaus Mountains (Himalayas). The coastline is poorly understood, and the characteristic subcontinent is difficult to recognize. The island of Taprobana (construed as Sri Lanka, believed by later geographers to be Sumatra) is placed further west than either of these candidates, but within its bounds, the map is detailed and accurate. For example, Palibotra (Patna) appears at the confluence of the Ganges and Son Rivers. The abundance of accurate placenames reflects the extent to which the Roman world was engaging with India in the Ptolemaic and pre-Ptolemaic periods.A New Ptolemy
This map appeared in the 1513 edition of Claudius Ptolemy's Geographia, whose translation and maps were the collaboration of Martin Waldseemüller and Matthias Ringmann, a duo best known for their 1507 world map, Universalis Cosmographia. Starting with the maps printed in the 1482 Ulm Ptolemy, Waldseemüller and Ringmann consulted Greek and Latin sources to produce an authoritative, corrected edition of the classical proto-atlas. In addition to the 27 maps based strictly on Ptolemaic data, it included 20 Tabulae Modernae. Among these maps are the first printed maps to focus on regions unknown to Ptolemy, such as North America and southern Africa, but they also include maps of areas covered in Ptolemaic geography but with new topography and toponymy, such as the maps of Lorraine and the Upper Rhine (which Waldseemüller probably surveyed himself) and a map of Crete. Ironically, Waldseemüller's name did not appear in the published book, as he and Ringmann had had a falling out by 1513.Publication History and Census
This map was drawn between 1507 and 1513 by Martin Waldseemüller at the Gymnasium Vosagense, an association of humanist scholars formed in Saint-Dié under the patronage of the Duke of Lorraine. The map was included in the Gymnasium's Geographie Opus Novissima Traductione e Graecorum Archetypis, printed in 1513 by Johannes Schott (Strasbourg). Schott published a single further edition of the book in 1520. There were no alterations to this block, but the watermark here - a fleur with its outer points turned inward - appears consistent with a 1513 printing. We find four examples of this separate map listed in OCLC, three dated 1513 and one dated 1520. Rare to the private market.CartographerS
Martin Waldseemüller (September 11, 1470 - March 16, 1520) was a German cartographer, astronomer, and mathematician credited with creating, along with Matthias Ringmann, the first map to use the placename America. He was born in Wolfenweiler, near Freiburg im Breisgau. Waldseemüller studied at the University of Freiburg and, on April 25, 1507, became a member of the Gymnasium Vosagese at Saint-Dié. Martin Waldseemüller was a major proponent of theoretical or additive cartography. Unlike contemporary Portuguese and Spanish cartographers, who left maps blank where knowledge was lacking, Waldseemüller and his peers speculated based upon geographical theories to fill unknown parts of the map. He is best known for his Universalis Cosmographia a massive 12-part wall map of the world considered the first map to contain the name America, today dubbed as 'America's Birth Certificate'. This map also had significance on other levels, as it combined two previously unassociated geographical styles: Ptolemaic Cartography, based on an ancient Greek model, and the emergent 'carta marina', a type of map commonly used by European mariners in the late 15th and 16th centuries. It also extended the traditional Ptolemaic model westward to include the newly discovered continent of America, which Waldseemüller named after the person he considered most influential in its discovery, Amerigo Vespucci. When Waldseemüller died in 1520, he was a canon of the collegiate Church of Saint-Dié. In contemporary references his name is often Latinized as Martinus Ilacomylus, Ilacomilus, or Hylacomylus. More by this mapmaker...
Claudius Ptolemy (83 - 161 AD) is considered to be the father of cartography. A native of Alexandria living at the height of the Roman Empire, Ptolemy was renowned as a student of Astronomy and Geography. His work as an astronomer, as published in his Almagest, held considerable influence over western thought until Isaac Newton. His cartographic influence remains to this day. Ptolemy was the first to introduce projection techniques and to publish an atlas, the Geographiae. Ptolemy based his geographical and historical information on the "Geographiae" of Strabo, the cartographic materials assembled by Marinus of Tyre, and contemporary accounts provided by the many traders and navigators passing through Alexandria. Ptolemy's Geographiae was a groundbreaking achievement far in advance of any known pre-existent cartography, not for any accuracy in its data, but in his method. His projection of a conic portion of the globe on a grid, and his meticulous tabulation of the known cities and geographical features of his world, allowed scholars for the first time to produce a mathematical model of the world's surface. In this, Ptolemy's work provided the foundation for all mapmaking to follow. His errors in the estimation of the size of the globe (more than twenty percent too small) resulted in Columbus's fateful expedition to India in 1492.
Ptolemy's text was lost to Western Europe in the middle ages, but survived in the Arab world and was passed along to the Greek world. Although the original text almost certainly did not include maps, the instructions contained in the text of Ptolemy's Geographiae allowed the execution of such maps. When vellum and paper books became available, manuscript examples of Ptolemy began to include maps. The earliest known manuscript Geographias survive from the fourteenth century; of Ptolemies that have come down to us today are based upon the manuscript editions produced in the mid 15th century by Donnus Nicolaus Germanus, who provided the basis for all but one of the printed fifteenth century editions of the work. Learn More...