This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
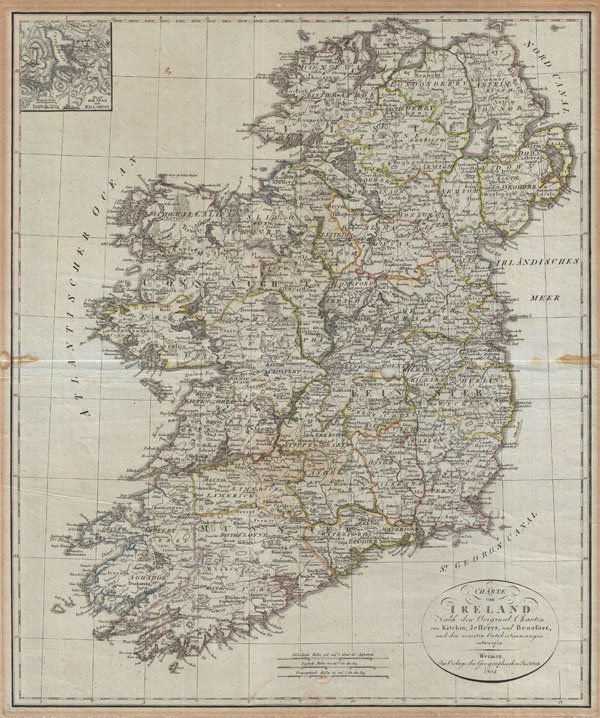
1804 Jeffreys and Kitchin Map of Ireland
Ireland-weimar-1804
Title
1804 (dated) 23 x 19 in (58.42 x 48.26 cm)
Description
CartographerS
Geographisches Institut, Weimar (fl. 1804 - c. 1903) was a German map and globe publishing house and geographical research institute based in Weimar. The organization primarily focused on republishing and improving upon the works of earlier cartographers, including Kitchin, Jefferys, Carey, and others. In general, its publications are known for their fine engraving, attention to detail, historical accuracy, and overall high quality. The firm was founded in 1804 by Friedrich Justin Bertuch (???? - c. 1845) and, on his death, passed to his son Robert Froreip (???? - 1855), then to Louis Denicks of Luneberg, then in 1859 to Voigt & Günther, in 1883 to F. Arnd, from 1890 - 1893 to Julius Kettler, and in 1903 to Max Wedekind. During the institute's height in the early 19th century, most of its cartographic publication was overseen by Carl Ferdinand Weiland (1782 - 1847). The firm also employed the cartographers Franz Xaver von Zach, Adam Christian Gaspari, Heinrich Kiepert, Karl (or Carl) and Adolf Graef, Julius Kettler, Carl Riemer and Karl Christian Bruhns. Weimar was a logical place for a collective like the Geographisches Institut to arise; it was a cultural mecca in the German-speaking world in the late 18th and 19th centuries because of its liberal atmosphere and associations with figures like Schiller, Herder, and, above all, Goethe, who spent most of his adult life in the city. More by this mapmaker...
Thomas Jefferys (1695 - November 20, 1771) was one of the most prominent and prolific map publishers and engravers of his day. Jefferys was born in Birmingham and was apprenticed to the engraver Emmanuel Bowen in 1735. Later, in the 1740s he engraved several maps for the popular periodical Gentleman's Magazine. Around 1740 Jefferys was finally able to go into business for himself and in 1746 received an appointment as 'Geographer to Fredrick, Prince of Wales,' which shortly after translated to the position of 'Royal Cartographer to King George III.' Jefferys initially specialized in compiling and re-engraving the works of earlier cartographers into more coherent cartographic wholes. Later, while not salaried position, Jefferys' appointment as 'Royal Cartographer' guaranteed preferential access to the most up to date cartographic material available, allowing him to produce new and updated charts of exceptional accuracy. He his best known for his maps of the Americas, particularly the posthumously published 1775 American Atlas, which included some of the finest and most important late colonial era maps of America ever made. Despite his prolific publishing history, royal appointments, and international publishing fame, Jefferys lived most of his life in dire economic straits. He was bailed out of bankruptcy by Robert Sayer during the production of the American Atlas. In the end, Jefferys died suddenly with very little to his name. Nonetheless, his cartographic legacy survived, and even after his death in 1771, many of his important maps continued to be published and republished by Sayer and Bennet, Conrad Lotter, Georges Louis Le Rouge, Laurie and Whittle, and others. Many attribute some of Jefferys best maps to the colorful and criminally inclined Irish cartographic genius Braddock Mead (John Green, c. 1688 - 1757), who is considered the 'secret behind Jefferys.' Jefferys was succeeded by his son, also Thomas, who had little success as a cartographer and eventually partnered with, then sold his stock and plates to William Faden - Jefferys' true heir. Learn More...
Thomas Kitchin (August 4, 1718 – June 23, 1784) was a London based engraver, cartographer, and publisher. He was born in London to a hat-dyer of the same name. At 14, Kitchin apprenticed under Emanuel Bowen, under whom he mastered the art of engraving. He married Bowen daughter, Sarah Bowen, and later inherited much of his preceptor's prosperous business. Their son, Thomas Bowen Kitchin, also an engraver joined the family business, which thereafter published in Thomas Kitchin and Son. From 1858 or so Kitchin was the engraver to the Duke of York, and from about 1773 acquired the title, 'Royal Hydrographer to King George III.' He is responsible for numerous maps published in the The Star, Gentleman's Magazine, and London Magazine, as well as partnering with, at various times, with Thomas Jefferys, Emmanuel Bowen, Thomas Hinton, Issac Tayor, Andrew Dury, John Rocque, Louis de la Rochette, and Alexander Hogg, among others. Kitchin passed his business on to his son, Thomas Bowen Kitchin, who continued to republish many of his maps well after his death. Kitchin's apprentices included George Rollos, Bryant Lodge, Thomas Bowen Kitchin, Samuel Turner Sparrow, John Page, and Francis Vivares. Learn More...