This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
1721 De Wit / Covens and Mortier Map of Italy
Italiae-covensmortier-1721
Title
1721 (undated) 19.5 x 23 in (49.53 x 58.42 cm) 1 : 2400000
Description
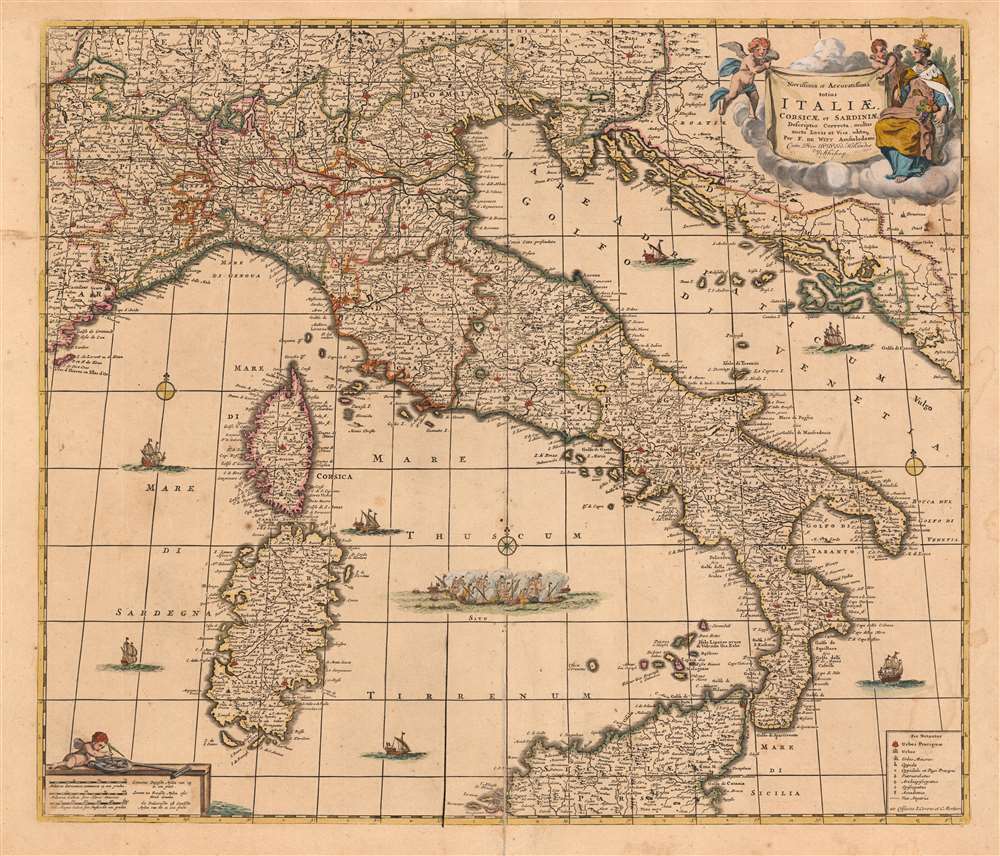
The Crypto-Island of 'M. Sardo'
As authoritative as Magini's 1608 wall map Italia Nuova was, one of its hallmarks was the placement of a mysterious mountainous island, 'M. Sardo', in the Gulf of Taranto. Despite being reproduced faithfully on near every 17th century map of the peninsula, the origins of this imaginary island have long been obscure. More recently, the scholar/collector Vladimirio Valerio discovered a notation on the Otranto map in the 1595 Stigliola manuscript Atlas of the Kingdom of Naples (added to his collection in 1975). On that manuscript, a crude mountain-hump is mapped in the Gulf of Taranto - the first known instance in print or otherwise of any such 'M. Sardo' in those waters. While no such island or mountain actually exists, there is, near the tip of Otranto, a mountaintop village - Monte Sardo - notable for its visibility both from the Gulf of Otranto and the Gulf of Venice. Thus the manuscript 'M. Sardo' is a crude coastal profile highlighting an observable coastal navigational feature. Valerio theorizes that, in compiling his masterpiece map of Italy, Magini consulted the Stigliola as the best and most detailed map of southern Italy. In doing so, he misinterpreted the navigational notation, preserving it as a literal mountain in the middle of the Gulf, and retaining the name M. Sardo. Magini's work was so authoritative that Blaeu copied the map, errors and all; and in turn, with few exceptions, the rest of the European mapmaking community followed.New Information
In 1695, the Italian mapmaker Cantelli da Vignola produced a new map of Italy. While its outline largely retained Magini's cartography, it focused specifically on the system of Post Roads linking Italy's kingdoms with the Holy Roman Empire. Consequently, Cantelli rendered Italy's cities and mountains very differently from maps based more entirely on Magini. Either Peter Mortier, having acquired De Wit's copperplates from his widow Maria, or his heir Cornelis Mortier would extensively amend De Wit's map to include Cantelli's Post Roads as well as a multitude of additional place names, particularly along the coastline.In The Dutch Tradition
The map is richly decorative, with a beautiful allegorical cartouche in the upper right featuring two putti on the wing and a seated, imperial woman, with a castle-crown surmounted with a star: Italia Turrita e Stellata, 'turreted and stellate Italy,' the allegorical personification of Italy. Seated with a cornucopia at her side, the Italia Turrita is an icon of Italian civic heraldry. Her walled crown appears in the iconography of many Italian cities, symbolically conveying the royalty and nobility of Italy as well as its agricultural abundance, and its notionally 'stellar' destiny.Highly Decorative
On a scale less grand, in the lower left the scales of the map are given in French, Italian and German miles. These are displayed on a plinth, upon which a third putto plays with navigational instruments. De Wit's seas are plied by seven superbly engraved ships, and a fierce naval battle is shown in the Tyrrhenian Sea. Covens and Mortier have retained all these elements whilst adding two extra compass roses, and letters in the margin for use as coordinates. They have added a key on the lower right not present on the original De Wit as well, showing the symbols used on the map to indicate cities of varying sizes, bishoprics and archbishoprics, forts, and the roads.Publication History and Census
De Wit's original engraving was done in and around 1680, the map being included in his atlases. After his death, the plate was sold to Peter Mortier, and reissued (thus amended) by his successors Covens and Mortier. We see only three examples of this map catalogued in OCLC, appearing in the University of Bern, the Bibliotheek Universiteit van Amsterdam, and the Sachische Landesbibliothek.CartographerS
Frederik de Wit (1629 - 1706) was a Dutch Golden Age cartographer active in the second half of the 17th and the early 18th centuries. De Wit was born of middle class Protestant stock in the western Netherlandish town of Gouda. He relocated to Amsterdam sometime before 1648, where he worked under Willem Blaeu. His first attributed engraved map, a plan of Haarlem for Antonius Sanderus' Flandria Illustrata, was issued around this time. He struck out on his own in 1654. The first chart that De Wit personally both drew and engraved was most likely his 1659 map of Denmark, REGNI DANIÆ Accuratissima delineatio Perfeckte Kaerte van ‘t CONJNCKRYCK DENEMARCKEN. His great wall map of the world and most famous work, Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula appeared one year later. Following the publication of his wall map De Wit quickly rose in prominence as a both cartographer and engraver. He married Maria van der Way in 1661 and through her became a citizen of Amsterdam in 1662. Around this time he also published his first major atlas, a composite production ranging in size from 17 to over 150 maps and charts. Other atlases and individual maps followed. In 1689 De Wit was granted a 15 year Privilege by the Dutch States General. (An early copyright that protected the recipient's rights to print and publish.) He was recognized with the honorific 'Good Citizen' in 1694. De Wit died in 1706 after which his wife Maria continued publishing his maps until about 1710. De Wit's son, Franciscus, had no interest in the map trade, instead choosing to prosper as a stockfish merchant. On her own retirement, Maria sold most De Wit maps and plates at a public auction. Most were acquired by Pieter Mortier and laid the groundwork for the 1721 rise of Covens and Mortier, the largest Dutch cartographic publishing house of the 18th century. More by this mapmaker...
Covens and Mortier (1721 - c. 1862) was an Amsterdam publishing firm, the successor to the extensive publishing empire built by Pierre Mortier (1661 - 1711). Covens and Mortier maps are often criticized as derivative - but this is not fully the case. Pierre Mortier lived in Paris from 1681 to 1685. There he established close relationships the the greatest French cartographers of the era, including De L'Isle and D'Anville. His business model was based upon leveraging Dutch printing technology and sophistication to co-publish state of the art French cartography. Upon Mortier's death in 1711 his firm was taken over by his son, Cornelius Mortier (1699 - 1783). Cornelius married the sister of Johannes Covens (1697 - 1774) in 1721 and, partnering with his brother in law, established the Covens and Mortier firm. Under the Covens and Mortier imprint, Cornelius and Johannes continued in Pierre's model of publishing the most up-to-date French works with permission. They quickly became one of the largest and most prolific Dutch publishing concerns of the 18th century. The firm and its successors published thousands of maps over a 120 year period from 1721 to the mid-1800s. During their long lifespan the Covens and Mortier firm published as Covens and Mortier (1721 - 1778), J. Covens and Son (1778 - 94) and Mortier, Covens and Son (1794 - c. 1862). Learn More...
Giovanni Antonio Magini (June 13, 1555 - February 11, 1617) was an Italian astronomer, astrologer, cartographer, and mathematician. Born in Padua, he completed his studies in philosophy in Bologna in 1579. In 1588 he was chosen over Galileo Galilei as the chair of mathematics at the University of Bologna after the death of Egnatio Danti. Magini was a prolific writer, putting forth theories of celestial motion (he was a supporter of a geocentric solar system), the use of quadrants in surveying and astronomy, and trigonometry. In 1608, Magini produced the first map of Italy to improve on that of Gastaldi: his meticulously researched and beautifully engraved 8-sheet Italia Nuova was hugely influential: upon its publication, Blaeu promptly copied it to produce his own wall map of Italy; the rest of the mapmaking establishment swiftly followed suit. Consequently, virtually every 17th century map of Italy can be identified as a derivative of Magini's monumental achievement. His atlas, Atlante geografico d’Italia, was published posthumously by his son in 1620. This work was intended to include maps of every Italian region with exact nomenclature and historical notes. He also served as court astrologer for the Duke of Mantua. Learn More...
Giacomo Cantelli da Vignola (February 22, 1643 - November 30, 1695) was an important Italian cartographer and engraver active in 17th century Italy. Cantelli was born in Montorsello, near Vignola, Italy to a prominent local family. After studying literature at the University of Bologna, Cantelli took a position as secretary to the Marquis Obizzi de Ferrara. Eventually Cantelli relocated to Venice where he developed an interest in cartography. He later traveled to Paris in the company of the French ambassador where became acquainted with the French cartographer Guillaume Sanson, as well as his contemporaries Jacques-Andre Duval and Michel-Antoin Baudrand. It was most likely the influence of these innovative French cartographers that inspired Cantelli's careful and meticulous approach, in which he based his cartography not just on earlier maps, but also very much in the French style upon accounts written by travelers and merchants regarding actual travel to foreign lands. Back in Italy, Cantelli took service with Count Rinieri Marescotti, with whom he traveled extensively throughout Italy, becoming in the process acquainted with the Italian publisher Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi. It is with Rossi that Cantelli began officially publishing his maps. The earliest maps to bear the Cantelli-Rossi imprint date to 1672 and detail the Holy Land, Persia, and the Ottoman Empire. Around 1680 the duo also began to publish the Mercurio Geografico, a large format atlas illustrating all parts of the world in a splendid Italian baroque detail defined by elaborate finely engraved cartouche work, high quality paper, bold Roman lettering, and dark rich inks. Some have compared his style go that of Giovanni Antonio Magini, another Italian cartographer of the previous generation. Cantelli da Vignola in fact pioneered the Italian style of fine bold engraving that would eventually be embraced and expanded upon by Vincenzo Coronelli. His work drew the attention of Pope Innocent XI and Reggio Francesco II d'Este, the Duke of Modena, both of whom offered him a position as court geographer. Cantelli chose to work with the Duke of Modena, in the service of whom he produced numerous maps and well as two large globes. He died in Modena in November 1695. Learn More...