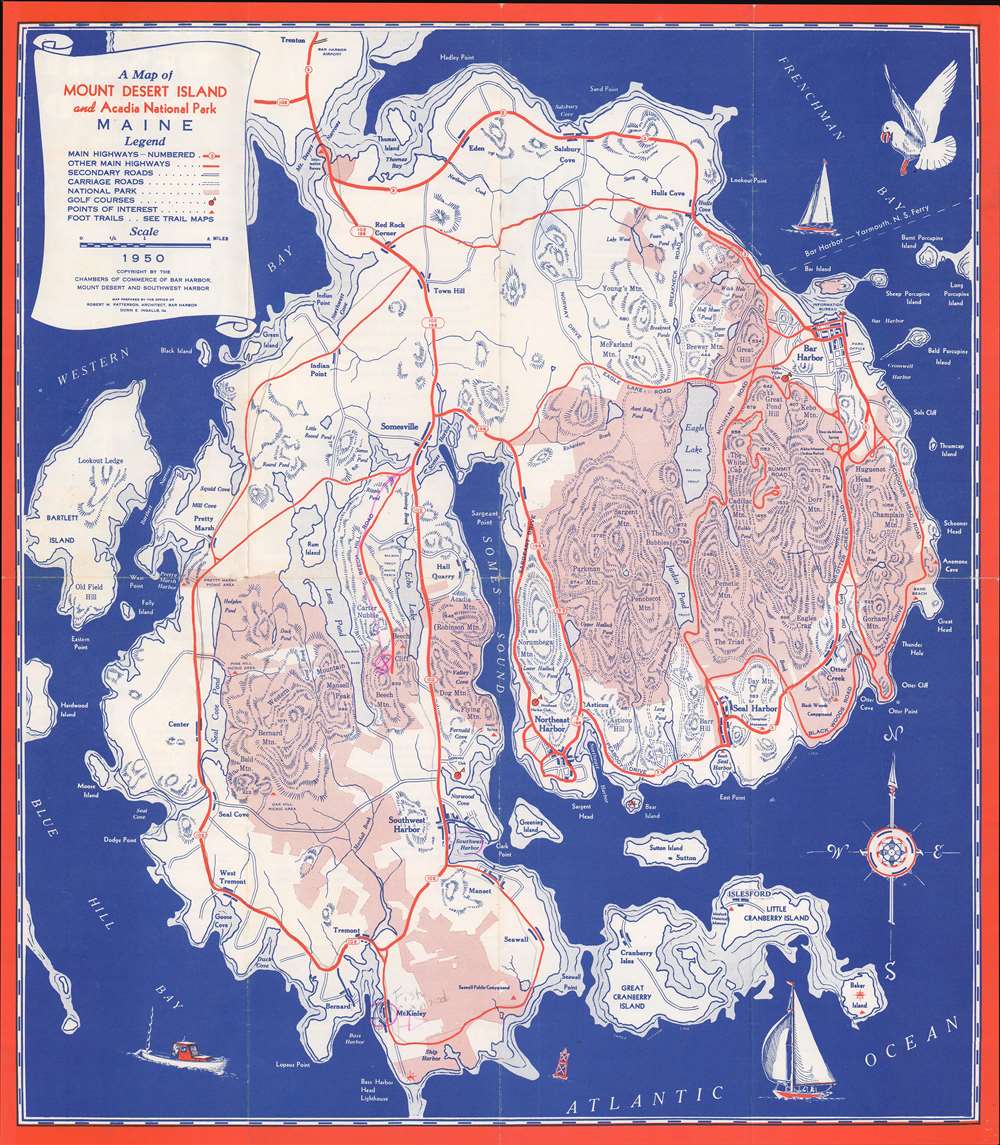
1950 National Survey Company Map of Mount Desert Island, Maine
MountDesertIsland-nationalsurveyco-1950
Title
1950 (dated) 17.75 x 15.75 in (45.085 x 40.005 cm) 1 : 56320
Description
Mount Desert Island
Popularized as a vacation destination during the 19th century, Mount Desert Island is renowned for its exceptional natural beauty. First brought to public attention by painters of the Hudson River School, tourists and nature lovers began flocking to the island in the 1860s. By 1880, the island hosted thirty grand hotels. By the 'Gay Nineties', American social elites and business magnates, including the Rockefellers, Fords, Vanderbilts, and Carnegies, built summer homes on the islands' most desirable land. Eventually the Rockefellers acquired most of the island, donating it to the Federal government as a public recreation area, Acadia National Park.Acadia National Park
Mount Desert Island, so named because of its many bald rocky mountaintops, has been a tourist destination since the mid-19th century, when it was discovered by outsiders, artists, journalists, Hudson River School artists, and other patrons, known collectively as the 'Rusticators.' Undaunted by crude accommodations and simple food, they sought out local fishermen and farmers for accommodation and guidance. Summer after summer, the rusticators returned to renew friendships with local islanders and, most of all, to savor the fresh salt air, scenery, and relaxed pace. Soon the villagers' cottages and fishermen's huts filled to overflowing, and by 1880, 30 hotels competed for vacationers' dollars. Tourism was becoming the islands primary industry. Drawing the attention of the wealthy and influential, the island was designated as Sieur de Monts National Monument by President Woodrow Wilson in July 1916. In February 1919, the area's status was officially changed from a National Monument to National Park, making it the first National Park east of the Mississippi River. With the change to a National Park came a name change as well, to Lafayette National Park. It was not until January 1929 that the park was given its current name, Acadia National Park. Acadia is unlike most other National Parks as its creation was encouraged by numerous private individuals. One, John. D. Rockefeller, purchased a summer home in Bass Harbor in 1910. Rockefeller began buying up land on the island with the goal of creating a system of carriage roads to make 'one of the greatest views in the world' accessible to all.Publication History and Census
This map was created by the National Survey Company and published by the Mount Desert Island Chamber of Commerce. Three examples are cataloged in OCLC and are part of the institutional collections at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Harvard University, and Pennsylvania State University.Cartographer
The National Survey Company (1912 - 2000) was a map publishing firm based in Chester, Vermont, founded by Lawton V. and Henry F. Crocker in 1912. The Crockers began their careers in the map trade as part-time summer traveling salesmen for The Bullard Company of Boston. However, their relationship with Bullard fell apart in 1912, which forced the brothers to found their own company. They created and published their own maps, with a series of detailed road maps leading to early success. They published maps in varying formats, from pocket maps to wall maps to road atlases. However, the free promotional oil company maps published in the 1920s by firms like Rand McNally almost forced National Survey out of the market. At this point they moved to Chester, Vermont, narrowly avoided bankruptcy, and refocused. They began creating their own promotional maps and travel publications, mainly for hotel and motel chains in New England. During World War II, they completely changed tactics again, and exclusively focused on war production. They published topographic maps for the Army Map Service and nautical charts for the Navy's Hydrographic Office. Work for the Army and Navy continued after the war, even with a renewed focus on tourist maps and guides. In 2000, National Survey was bought by Universal Map, who chose to continue operating out of Chester, Vermont. More by this mapmaker...