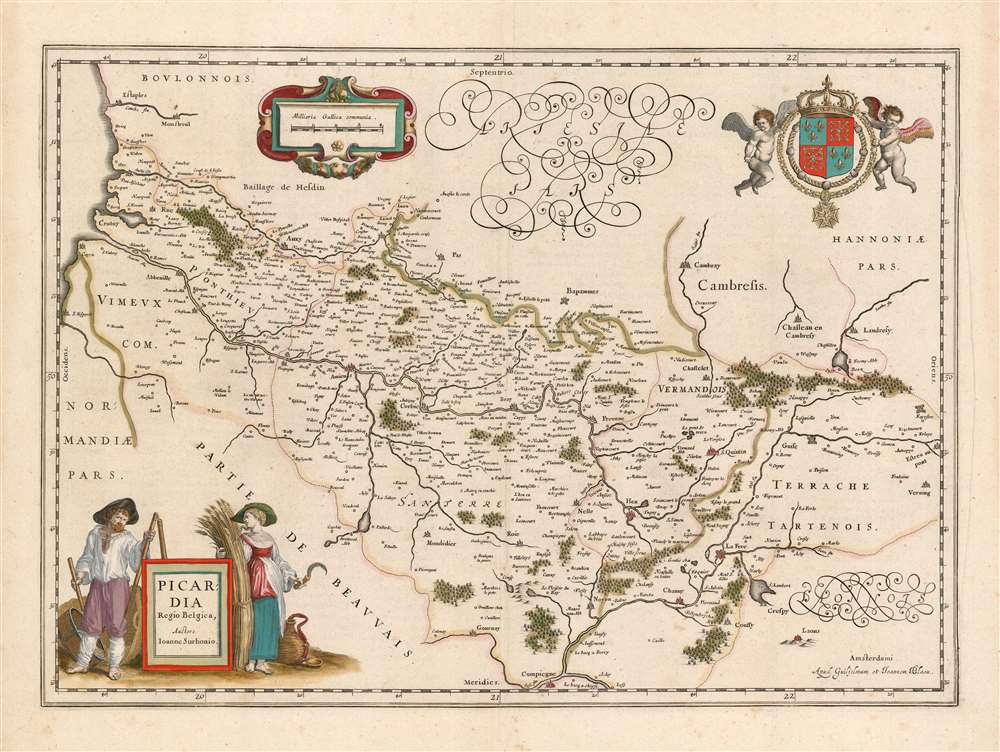
1644 Blaeu Map of Picardy
Picardy-blaeu-1644
Title
1644 (undated) 15 x 20.75 in (38.1 x 52.705 cm) 1 : 335000
Description
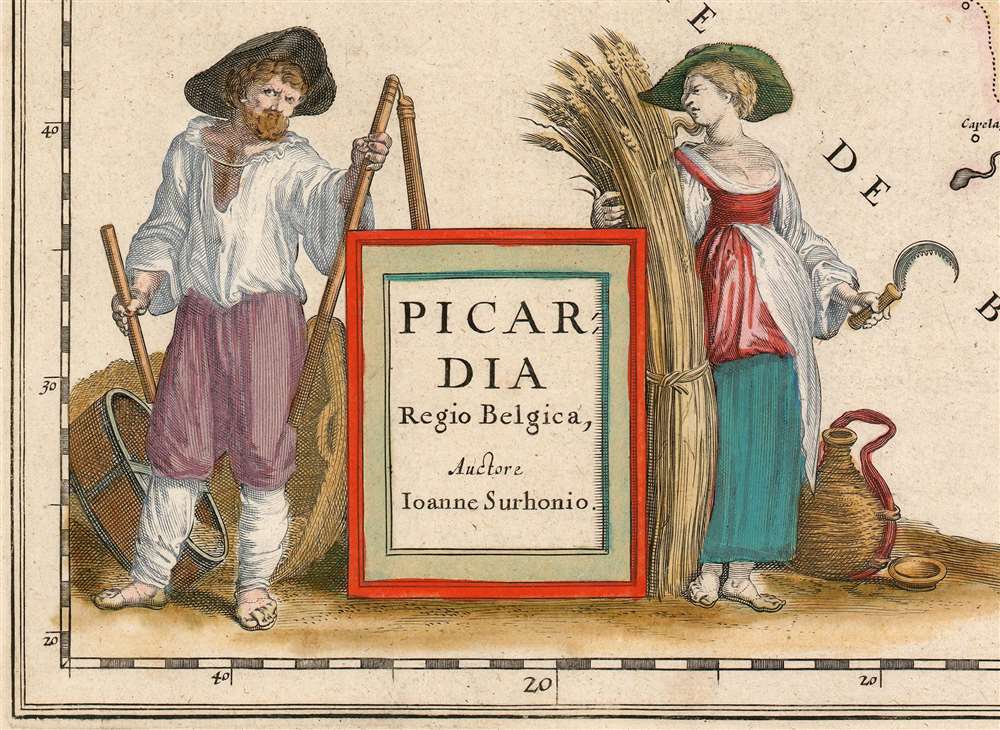
The Farmer and His Wife
The map's title cartouche is graced with an astonishingly homely and evocative scene. It is flanked by a farmer and a woman who, by her expression of pointed anger, can only be his wife. Sickle in hand, she glares at him while he peers at the reader under furrowed brows. This writer's spouse was alarmingly quick to assess the scene: 'He didn't do what he was supposed to do with the wheat, and she's annoyed because now she has to do it.'While the story told in this vignette appears to be plain enough, its context here is obscure. Why are this woebegone husband and his infuriated wife being associated with Picardy? There are many folk tales playing variations on the theme of The Farmer and His Wife - is there a specific one being alluded to? It would not be the only time a sly allusion to the politics of a region would be slipped into the decorations of a map. It may be a simple jibe by sophisticated Amsterdammers at the expense of the rustic denizens of a contested borderland.
The Source
The cartography itself is not innovative: Blaeu's map is a faithful reproduction of Jean de Surhon's 1557 map, as presented in Abraham Ortelius' 1579 Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. Both great atlas makers were keener surveyors of cartographic sources, than of the lands themselves.Belgica not Gallia
Jean de Surhon produced his map in 1557, the year in which Picardy was invaded by Habsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy during the so-called Italian War between France and the Holy Roman Empire. The campaigns in Picardy would be marked by pronounced Habsburg victories, in particular that of the The Battle of Saint-Quentin of 1557. Therefore at the time Surhon's map was produced, Picardy was not so much part of France (Gallia) as it was part of The Habsburg Netherlands (Belgica.) The 1559 Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis, however, would return St. Quentin and the lands of the Somme to the French - hence the French coat of arms decorating the map.Publication History and Census
This map first appeared in Blaeu’s Atlas Novusin 1635, continuing to appear in that work until it was replaced by Joan Blaeu's updated - yet relatively charmless - map for his Atlas Maior. This example appeared in one of the Latin editions of Atlas Novus, between 1644 and 1655. There are about fifteen examples of the separate map cataloged in institutional collections.CartographerS
Willem Janszoon Blaeu (1571 - October 18, 1638), also known as Guillaume Blaeu and Guiljelmus Janssonius Caesius, was a Dutch cartographer, globemaker, and astronomer active in Amsterdam during the late 16th and early 17th centuries. Blaeu was born 'Willem Janszoon' in Alkmaar, North Holland to a prosperous herring packing and trading family of Dutch Reformist faith. As a young man, he was sent to Amsterdam to apprentice in the family business, but he found the herring trade dull and instead worked for his cousin 'Hooft' as a carpenter and clerk. In 1595, he traveled to the small Swedish island of Hven to study astronomy under the Danish Enlightenment polymath Tycho Brahe. For six months he studied astronomy, cartography, instrument making, globe making, and geodesy. He returned to Alkmaar in 1596 to marry and for the birth of his first son, Johannes (Joan) Blaeu (1596 – 1673). Shortly thereafter, in 1598 or 1599, he relocated his family to Amsterdam where he founded the a firm as globe and instrument makers. Many of his earliest imprints, from roughly form 1599 - 1633, bear the imprint 'Guiljelmus Janssonius Caesius' or simply 'G: Jansonius'. In 1613, Johannes Janssonius, also a mapmaker, married Elizabeth Hondius, the daughter of Willem's primary competitor Jodocus Hondius the Elder, and moved to the same neighborhood. This led to considerable confusion and may have spurred Willam Janszoon to adopt the 'Blaeu' patronym. All maps after 1633 bear the Guiljelmus Blaeu imprint. Around this time, he also began issuing separate issue nautical charts and wall maps – which as we see from Vermeer's paintings were popular with Dutch merchants as decorative items – and invented the Dutch Printing Press. As a non-Calvinist Blaeu was a persona non grata to the ruling elite and so he partnered with Hessel Gerritsz to develop his business. In 1619, Blaeu arranged for Gerritsz to be appointed official cartographer to the VOC, an extremely lucrative position that that, in the slightly more liberal environment of the 1630s, he managed to see passed to his eldest son, Johannes. In 1633, he was also appointed official cartographer of the Dutch Republic. Blaeu's most significant work is his 1635 publication of the Theatrum orbis terrarum, sive, Atlas Novus, one of the greatest atlases of all time. He died three years later, in 1638, passing the Blaeu firm on to his two sons, Cornelius (1616 - 1648) and Johannes Blaeu (September 23, 1596 - December 21, 1673). Under his sons, the firm continued to prosper until the 1672 Great Fire of Amsterdam destroyed their offices and most of their printing plates. Willem's most enduring legacy was most likely the VOC contract, which ultimately passed to Johannes' son, Johannes II, who held the position until 1617. As a hobbyist astronomer, Blaeu discovered the star now known as P. Cygni. More by this mapmaker...
Joan (Johannes) Blaeu (September 23, 1596 - December 21, 1673) was a Dutch cartographer active in the 17th century. Joan was the son of Willem Janszoon Blaeu, founder of the Blaeu firm. Like his father Willem, Johannes was born in Alkmaar, North Holland. He studied Law, attaining a doctorate, before moving to Amsterdam to join the family mapmaking business. In 1633, Willem arranged for Johannes to take over Hessel Gerritsz's position as the official chartmaker of the Dutch East India Company, although little is known of his work for that organization, which was by contract and oath secretive. What is known is his work supplying the fabulously wealthy VOC with charts was exceedingly profitable. Where other cartographers often fell into financial ruin, the Blaeu firm thrived. It was most likely those profits that allowed the firm to publish the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, sive, Atlas Novus, their most significant and best-known publication. When Willem Blaeu died in 1638, Johannes, along with his brother Cornelius Blaeu (1616 - 1648) took over the management of the Blaeu firm. In 1662, Joan and Cornelius produced a vastly expanded and updated work, the Atlas Maior, whose handful of editions ranged from 9 to an astonishing 12 volumes. Under the brothers' capable management, the firm continued to prosper until the 1672 Great Amsterdam Fire destroyed their offices and most of their printing plates. Johannes Blaeu, witnessing the destruction of his life's work, died in despondence the following year. He is buried in the Dutch Reformist cemetery of Westerkerk. Johannes Blaeu was survived by his son, also Johannes but commonly called Joan II, who inherited the family's VOC contract, for whom he compiled maps until 1712. Learn More...
Abraham Ortelius (April 14, 1527 - June 28, 1598) also known as Ortels, was a cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer of Brabant, active in Antwerp. He was the creator of the first modern atlas, Theatrum Orbis Terrarum and is a seminal figure in the history of cartography. Along with Gerard Mercator and Gemma Frisius, he was a founder of the Netherlandish school of cartography. His connections with Spain - culminating in his 1575 appointment as Royal Cartographer to King Phillip II of Spain - gave him unmatched access to Spanish geographical knowledge during a crucial period of the Age of Discovery. Ortelius was born in 1527 in Antwerp. In 1547 he entered the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke as an illuminator of maps. He began trading in books, prints, and maps, traveling regularly to the Frankfurt book and print fair, where in 1554 he met Mercator. He accompanied Mercator on journeys throughout France in 1560 and it was at this time, under Mercator's influence, that he appears to have chosen his career as a scientific geographer. His first published geographic work appeared in 1564, an eight-sheet cordiform world map. A handful of other maps preceded the 1570 publication of the first edition of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, which would prove to be his life work. Appearing with but 53 maps in its first edition, Ortelius' work expanded with new maps added regularly. By 1592, it had 134 maps. Many of Ortelius' maps remained the standard for nearly a century. He traveled extensively, but his genius was as a compiler, locating the best informed maps on which to base his own. His contacts throughout Europe and extending even (via the Portuguese) to the Far East were formidable. Moreover, many of his maps were based on his own scholarship, particularly his historical works. His theories of geography were particularly ahead of his time with respect to the notion of continental drift, the possibility of which he mused on as early as 1596, and which would be proven correct centuries later.
In a sense his greatest achievement was his successful navigation of the religious and political violence endemic to his city throughout his adult life: The Dutch Revolt, or Eighty Years' War (1568 - 1648), fully embroiled Antwerp. Although outwardly and officially recognized as Catholic (Arias Montanus vouched for Ortelius' Catholic orthodoxy prior to his appointment as Royal Geographer), Ortelius was able to separate himself from the religious furor which characterized the war in the low countries. Ortelius showed a glimpse of himself in a letter to a friend, regarding humanist Justus Lipsius: 'I do not know whether he is an adherent of the Pope or a Calvinist, but if he has ears to hear, he will neither be one nor the other, for sins are committed on both sides'. Ortelius' own explorations of Biblical history in his maps, and the Christogram contained in his own motto, suggest him to be a religious man, but his abjuration of political religious authorities mark him as an individualist. His tombstone at St Michael's Præmonstratensian Abbey in Antwerp bears the inscription, Quietis cultor sine lite, uxore, prole. ('served quietly, without accusation, wife, and offspring.') Learn More...
Jean de Surhon (fl. 1550 - 1600) was a Franco-Flemish engraver and cartographer. His father and brother, both named Jacques, were engravers and cartographers as well: his father was also a silversmith. He is remembered for those of his maps which were incorporated in Ortelius' Theatrum Orbis Terrarum: those of Namur (1553), Vermandois (1557), Luxembourg (1551), and Picardy (1557). The original maps do not appear to have survived, and thus Ortelius' versions are the earliest acquirable to the collector. The first, 1570 edition of the Theatrum contained the map of Vermandois: Namur and Picardy first appeared in the 1579 edition. It is a testament to Surhon's maps that no improvement was made to them until the second half of the seventeenth century: Willem Blaeu's atlas would reprise Surhon's work in a faithful, though more beautiful copy of the Ortelius. Learn More...