This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
1707 J. B. Homann Double Hemisphere World Map
World-Homann-1707
Title
1707 (undated) 19 x 22.25 in (48.26 x 56.515 cm) 1 : 90000000
Description
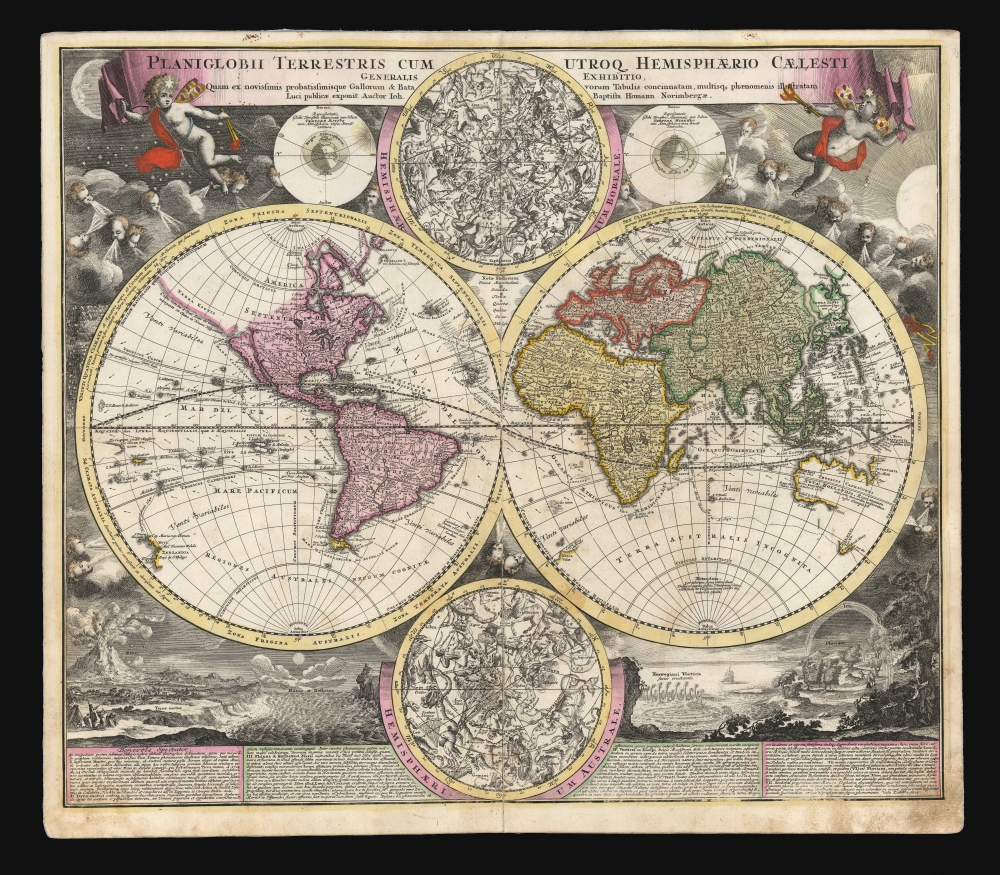
A Closer Look
In its generalities, the map evokes the Dutch maps of the previous century, featuring an insular California and a depiction of Australia and the South Pacific that resembles that of Abel Tasman. Homann nonetheless incorporated a significant detail from the state-of-the-art maps of the Parisian geographer Guillaume De l'Isle, and the English polymath Edmund Halley. The map is a rich compendium of explorers' routes, including Magellan, Tasman, Gaetani, and Chaumont, as well as the extremely current voyages of Dampier (whose discovery of Nova Britannia near New Guinea is shown with a date of 1700). Above and below the cruxes of the main hemispheres are a pair of celestial hemispheres. At the bottom is a beautifully engraved panorama illustrating volcanoes, earthquakes, the tides, marine vortices, rain, and rainbows. These themes are significant in that they are neither mythological nor allegorical: they are plainly discussed natural phenomena. The map, then, is a visual representation of a shift to a more modern, scientific approach to the study of the world that would be typical of the 18th century.The Sources
In the title of his map, Homann describes his sources as 'the latest and most approved maps of the French and the Dutch'. The bulk of Asia, Africa, and Europe appear to derive from the c. 1700 Peter Schenk Haemisphaeriorum Tabula Carthesiana, while the labeling scheme shows a strong similarity to the c. 1700 Danckerts De Werelt Caart. The primary French source is certainly Guillaume de l'Isle's 1700 Mappe-Monde. The explorers' tracks, the illustration of the Sargasso Sea, and an astonishing (and erroneous) sighting of Antarctica all derive from De l'Isle. Likewise with the treatment of the Pacific Northwest coast and Asiatic northeast, including the channel separating Terra Iesso from the mainland. Otherwise, the general models of Asia, Africa, and South America closely follow the c. 1700 Schenk.North America
The mapping of North America, here, is very different from either the Schenk or the 1700 De l'Isle. Although Homann retained California as an Island, the map was quite up to date. It presents a largely correct delineation of the Great Lakes and the Mississippi. The northwest part of Canada and the course of the Mississippi reveal the likely source: De l'Isle's 1703 Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France (including the Baron Lahontan's spurious geography) and De l'Isle's Carte du Mexique et de la Floride.A further plate of the map - probably re-engaved by Homann's heirs after the elder's death in 1724, and after receiving the Imperial privilege - replace the insular California with the less definitive form of California proposed by De l'Isle in his Mappe-Monde.
Halley's Winds
Another feature not appearing on either De l'Isle or the Dutch sources are the notations of the trade winds and the monsoons, derived from the recent work of Edmund Halley: this as far as we have seen is the earliest that these details are incorporated on a general world map.Two Steps Forward…
Much of the geography of the southern hemisphere follows suit with the double-hemisphere maps of the second half of the 17th century: Australia, for example, follows Tasman's model, albeit amended with notes pertaining to Dampier's expedition. As with almost all serious maps following Joan Blaeu's 1648 wall map, the present work dispenses with the Terra Australis Incognita which dominated the south in maps of the 16th century and the first half of the seventeenth.Almost.
At approximately 40°S, and about 5°E longitude as reckoned on the map, there appears a partial coastline entitled Terra Vitae, described further as Caput Terrae Australis (The land of Life, Head of the Southern Land). Homann copied this feature from De l'Isle Mappe-Monde - although he has made a transcription error. De l'Isle referred to the land in question, not as Terra Vitae, but as Terre De Vue (sighted land). He agrees, however, that the 'sighted land' was the northernmost shore of the long-sought-after Terra Australis Incognita. Sadly, the French geographer does not reveal his source and in any case, that part of the southern Atlantic is devoid of any such land. Perhaps, as Homann muses regarding the phantom island of Frisland, this land has been submerged.
A Masterwork of Engraving
The decorative engraving is of a very high quality throughout. In the upper part of the map, two burly putti support a broad title banner. In the background the daytime and nighttime skies are depicted; these scenes accompany diagrams illustrating the relationship between the angle of the Earth's axis and the seasonal changes of the sun's illumination of the globe. At bottom are two superbly engraved compositions describing an array of natural phenomena including volcanoes, whirlpools, rain, and rainbows. These are accompanied by explanatory text detailing each of these, including a discussion of Eduardus (sic) Halley's study of the trade winds and a description of a specific volcanic eruption in the Canary Islands, dated December 24, 1704.Precursor of the Zurner World Map
It will be noted that the scenes and descriptions of phenomena also appear on Adam Friedrich Zurner's Planisphaerium Terrestre cum utroque Coelesti Hemisphaerio, printed by Pieter Schenk, and that the body of the map is extremely similar to Zurner's. The Zurner is commonly dated c.1700 in blatant disregard of its content, which like the Homann includes a direct reference to a December 1704 volcanic eruption. This convention can be laid at the feet of Rodney Shirley, who selected that date perhaps in order to make the map fit the scheme of his book (which took as its end point the year 1700). It is shocking to suppose that Shirley hadn't read the map closely enough to see the evidence of a later date. Whatever the reason, most catalog listings of the Zurner bow to Shirley's authority, with the result that the map's actual date is not at all understood. In any case, any dating prior to 1705 is not credible for the Zurner.It is agreed that Zurner's world map made its appearance (accompanied by his maps of America and the other continents) in Schenk's Atlas Contractus, a work which was in print as early as 1700. Scrutinizing complete examples of the Atlas reveals that as late as 1703 none of Zurner's maps were present. The earliest example we have seen that contains Zurner's maps - including the world map in question - is a 1710 printing. The usual dating for the Zurner America map is 1709.
Comparison between the maps of the decorative, 'natural phenomena' scenes is telling. Those appearing on the Homann are remarkably finely-engraved, and smoothly-composed works - framed by the trees on the right, and the fearsome volcano on the left. The corresponding images appearing on Zurner's work are murky and cluttered in their engraving, with large portions obscured by, or moved to accommodate a pair of the many astronomical diagrams for which that map is justifiably famed. It is apparent to close inspection that the Zurner is copied from Homann, and not the other way around; considering a first publication date of 1707 for the Homann, a date of 1709 for Zurner's map is appropriate.
Publication History and Census
The present example of this map was included in a 1710 edition of Homann's Neuer Atlas. We see examples in institutional collections cataloged with dates as early as 1700 but given the content of the map these dates are not credible. We see no examples of Homann's Neuer Atlas earlier than 1707; thus, the present work remains an early printing of the map. This example, without a privilege and with California as an island, is the first plate of the map. We see this plate appearing in Homann atlases as late as 1716, and some later examples may have been produced. Most examples appearing on the market are of the later, post-privilege plate, entirely re-engraved by Homann's son Johann Christoph. In about 1735, Homann Heirs would replace the map entirely in the atlas with the very different Planiglobii Terrestris Mappe Monde. The separate map in its later printings is well represented in institutional collections, and appears on the market from time to time. This first plate appears much less frequently, although past poor cataloguing of Homann maps foils close analysis.CartographerS
Johann Baptist Homann (March 20, 1664 - July 1, 1724) was the most prominent and prolific map publisher of the 18th century. Homann was born in Oberkammlach, a small town near Kammlach, Bavaria, Germany. As a young man, Homann studied in a Jesuit school and nursed ambitions of becoming a Dominican priest. Nonetheless, he converted to Protestantism in 1687, when he was 23. It is not clear where he mastered engraving, but we believe it may have been in Amsterdam. Homann's earliest work we have identified is about 1689, and already exhibits a high degree of mastery. Around 1691, Homann moved to Nuremberg and registered as a notary. By this time, he was already making maps, and very good ones at that. He produced a map of the environs of Nürnberg in 1691/92, which suggests he was already a master engraver. Around 1693, Homann briefly relocated to Vienna, where he lived and studied printing and copper plate engraving until 1695. Until 1702, he worked in Nuremberg in the map trade under Jacob von Sandrart (1630 - 1708) and then David Funck (1642 - 1709). Afterward, he returned to Nuremberg, where, in 1702, he founded the commercial publishing firm that would bear his name. In the next five years, Homann produced hundreds of maps and developed a distinctive style characterized by heavy, detailed engraving, elaborate allegorical cartouche work, and vivid hand color. Due to the lower cost of printing in Germany, the Homann firm could undercut the dominant French and Dutch publishing houses while matching their diversity and quality. Despite copious output, Homann did not release his first major atlas until the 33-map Neuer Atlas of 1707, followed by a 60-map edition of 1710. By 1715, Homann's rising star caught the attention of the Holy Roman Emperor Charles VI, who appointed him Imperial Cartographer. In the same year, he was also appointed a member of the Royal Academy of Sciences in Berlin. Homann's prestigious title came with several significant advantages, including access to the most up-to-date cartographic information as well as the 'Privilege'. The Privilege was a type of early copyright offered to very few by the Holy Roman Emperor. Though less sophisticated than modern copyright legislation, the Privilege offered limited protection for several years. Most all J. B. Homann maps printed between 1715 and 1730 bear the inscription 'Cum Priviligio' or some variation. Following Homann's death in 1724, the firm's map plates and management passed to his son, Johann Christoph Homann (1703 - 1730). J. C. Homann, perhaps realizing that he would not long survive his father, stipulated in his will that the company would be inherited by his two head managers, Johann Georg Ebersberger (1695 - 1760) and Johann Michael Franz (1700 - 1761), and that it would publish only under the name 'Homann Heirs'. This designation, in various forms (Homannsche Heirs, Heritiers de Homann, Lat Homannianos Herod, Homannschen Erben, etc.) appears on maps from about 1731 onwards. The firm continued to publish maps in ever-diminishing quantities until the death of its last owner, Christoph Franz Fembo (1781 - 1848). More by this mapmaker...
The De L'Isle family (fl. c. 1700 - c. 1760) (also written Delisle) were, in composite, a mapmaking tour de force who redefined early 18th century European cartography. Claude De L'Isle (1644 -1720), the family patriarch, was Paris based a historian and geographer under Nicholas Sanson. De L'Isle and his sons were proponents of the school of "positive geography" and were definitive figures, defining the heights of the Golden Age of French Cartography. Of his twelve sons, four, Guillaume (1675 - 1726), Simon Claude (1675 - 1726), Joseph Nicholas (1688 - 1768) and Louis (1720 - 1745), made a significant contributions to cartography. Without a doubt Guillaume was the most remarkable member of the family. It is said that Guillaume's skill as a cartographer was so prodigious that he drew his first map at just nine years of age. He was tutored by J. D. Cassini in astronomy, science, mathematics and cartography. By applying these diverse disciplines to the vast stores of information provided by 18th century navigators, Guillaume created the technique that came to be known as "scientific cartography", essentially an extension of Sanson's "positive geography". This revolutionary approach transformed the field of cartography and created a more accurate picture of the world. Among Guillaume's many firsts are the first naming of Texas, the first correct map of the Mississippi, the final rejection of the insular California fallacy, and the first identification of the correct longitudes of America. Stylistically De L'Isle also initiated important changes to the medium, eschewing the flamboyant Dutch style of the previous century in favor of a highly detailed yet still decorative approach that yielded map both beautiful and informative. Guillaume was elected to the French Academie Royale des Sciences at 27. Later, in 1718, he was also appointed "Premier Geographe du Roi", an office created especially for him. De L'Isle personally financed the publication of most of his maps, hoping to make heavy royalties on their sales. Unfortunately he met an untimely death in 1728, leaving considerable debt and an impoverished child and widow. De L'Isle's publishing firm was taken over by his assistant, Phillipe Buache who became, posthumously, his son in law. The other De L'Isle brothers, Joseph Nicholas and Louis De L'Isle, were employed in the Service of Peter the Great of Russia as astronomers and surveyors. They are responsible for cataloguing and compiling the data obtained from Russian expeditions in the Pacific and along the northwest coast of America, including the seminal explorations of Vitus Bering and Aleksei Chirikov. The De L'Isles, like their rivals the Vaugondys , must be considered speculative geographers. Speculative geography was a genre of mapmaking that evolved in Europe, particularly Paris, in the middle to late 18th century. Cartographers in this genre would fill in unknown areas on their maps with speculations based upon their vast knowledge of cartography, personal geographical theories, and often dubious primary source material gathered by explorers and navigators. This approach, which attempted to use the known to validate the unknown, naturally engendered many rivalries. The era of speculatively cartography effectively ended with the late 18th century explorations of Captain Cook, Jean Francois de Galaup de La Perouse, and George Vancouver. Learn More...
Petrus Schenk (Pieter Schenck) the Elder (December 26, 1660 - 1711) was a Dutch engraver, globe maker, and map publisher active in Amsterdam and Leipzig in the latter half of the 17th century. Schenk, was born in Elberfield, Germany. He moved in Amsterdam in 1675, becoming the apprentice to Gerard Valk (Valck). In 1687, Schenk married Agatha Valk, Gerard Valk's sister and went into partnership with his brother-in-law under the imprint of 'Valk and Schenk'. Initially they focused on maps and atlases, acquiring the map plates of Jan Jansson and Jodocus Hondius in 1694. Later, in 1701 they moved into the former Hondius offices where they began producing globes. Valk and Schenk quickly became known for producing the best globes in the Netherlands, a business on which they held a near monopoly for nearly 50 years. Schenk's three sons, Pieter Schenk the Younger, Jan Schenk, and Leonard Schenk, all became engravers in their own right. Pieter Schenk the Younger inherited the business and ran his father's shop in Leipzig. His daughter, Maria Schenk, married Leonard Valk, the son of Gerard Valk, and continued to run the Valk and Schenk map engraving workshop in Amsterdam. Learn More...
Edmond (Edmund) Halley (November 8, 1656 - January 25, 1742) was an English astronomer, geophysicist, mathematician, meteorologist, and physicist. As Halley was such an accomplished individual, this biography will only be concerned with his contributions to cartography, of which there were many. Today, Halley is credited with the development of the earliest meteorological chart and the first printed isoline map. He also produced a map of the shadow of a solar eclipse that passed through London and a tidal chart. These maps are considered to be major contributions in thematic cartography. During the year 1686, Halley published four papers in the Philosophical Transactions. One of these, entitled 'An Historical Account of the Trade Winds, and Monsoons, observable in the Seas between and Near the Tropicks; with an attempt to assign the Phisical cause of the said Winds' was illustrated what has become known as the first meteorological chart. Although untitled, this map has come to be known as 'Halley's Chart of the Trade Winds'. Unaccompanied by a legend or a key, the only way to understand this map is to read Halley's article. The map lacks a scale, and the size of the grid varies, making Halley's first important map of the Earth difficult to interpret. In 1698, Halley was granted a temporary commission as a Captain in the Royal Navy and given command of the Paramour, a newly-built ship with the express purpose of test his magnetic theory in the southern hemisphere. Halley's voyage has become known as 'the first sea journey undertaken for a purely scientific object'. After being forced to return to Britain to deal with a mutinous crew, Halley set off anew in 1699 to test his theories. Following his return from more than a year aboard the Paramour, Halley published one of the most important maps in the history of cartography. Titled, 'A New and Correct Chart showing the Variations of the Compass in the Western and Southern Oceans' and based on over 150 observations on magnetic declination, this map is said to be the first printed map showing isotopes (lines of equal magnetic attraction). Per Norman Thrower
Halley's Atlantic chart is not only the first printed map of isogones, which were known as Halleyan lines for about a century, but it appears to be the earliest published isarithmic map of any kind. In quantitative cartography, isarithms (isolines) are lines, in series, connecting points of equal intensity of phenomena which have transitional degrees of intensity.Halley's Atlantic chart was not published to accompany an article, it was actually published as a sheet map and measured 22.5 x 19 inches. Halley's next contribution to the history of cartography was a much larger world chart along the same lines as his Atlantic chart. This chart measured 20 x 57 inches on a Mercator projection. Most of the innovations associated with the world chart are similar to those of the Atlantic chart, just on a larger scale. Halley also undertook a survey off the English Channel, entitled ' A New and Correct Chart of the Channel between England and France with considerable Improvements not extant in any Draughts hitherto Publish'd shewing the sands, shoals, depths of Water and Anchorage, with yet flowing of the Tydes, and the setting of the Current; as observed by the Learned Dr. Halley.' Spanning two sheets, each measuring 25 x 19 inches, this chart was likely published in 1702. The chart bears numerous notations and conventions common by Halley's time, but the feature that sets it apart from 'all previous charts' is the inclusion of the tides
Halley's final cartographic contribution deals with a map entitled 'A Description of the Passage of the Shadow of the Moon over England in the Total Eclipse of the Sun on the 22nd Day of April 1715 in the Morning'. The general map, in itself, is unremarkable, but the map's theme is both interesting and original. The map traces the path and shadow of the eclipse and indicates the time it took the eclipse to cross England. Learn More...